Types of Signalling
Cell signalling may involve the transmission of a chemical signal over a broad range of distances in order to elicit a response
-
Examples of intercellular communication within organisms include autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signalling
-
Additionally, certain chemicals may be transmitted between members of a species (e.g. pheromones) or between different species (e.g. allelopathy)
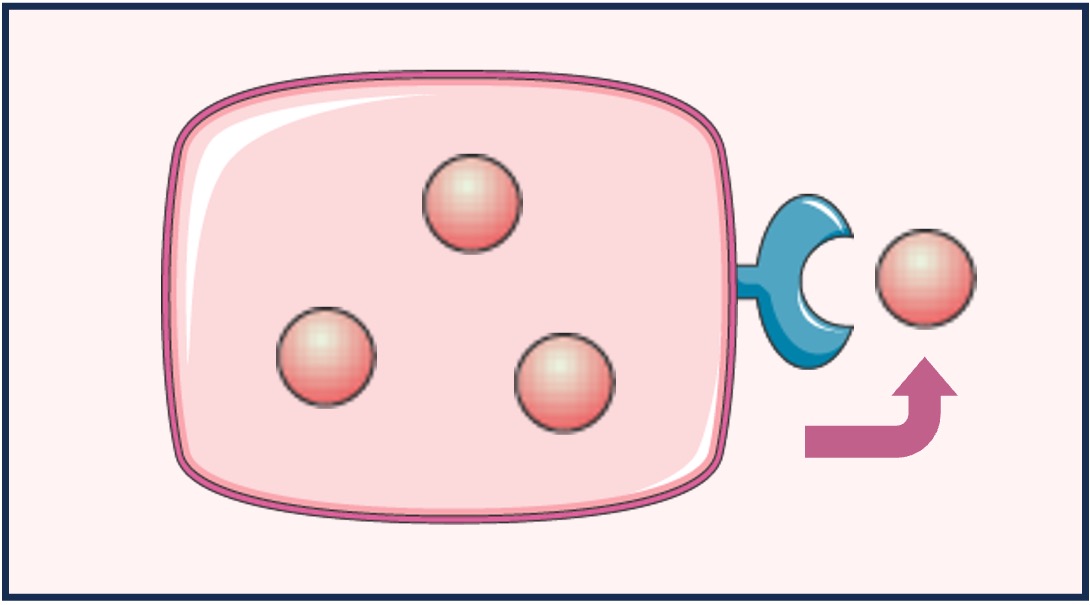
Autocrine
-
Autocrine signalling occurs when the chemicals released by a cell stimulate the cell itself (i.e. ‘self’ signalling)
-
An example is the proliferation of T lymphocytes following cytokine release from an activated T lymphocyte
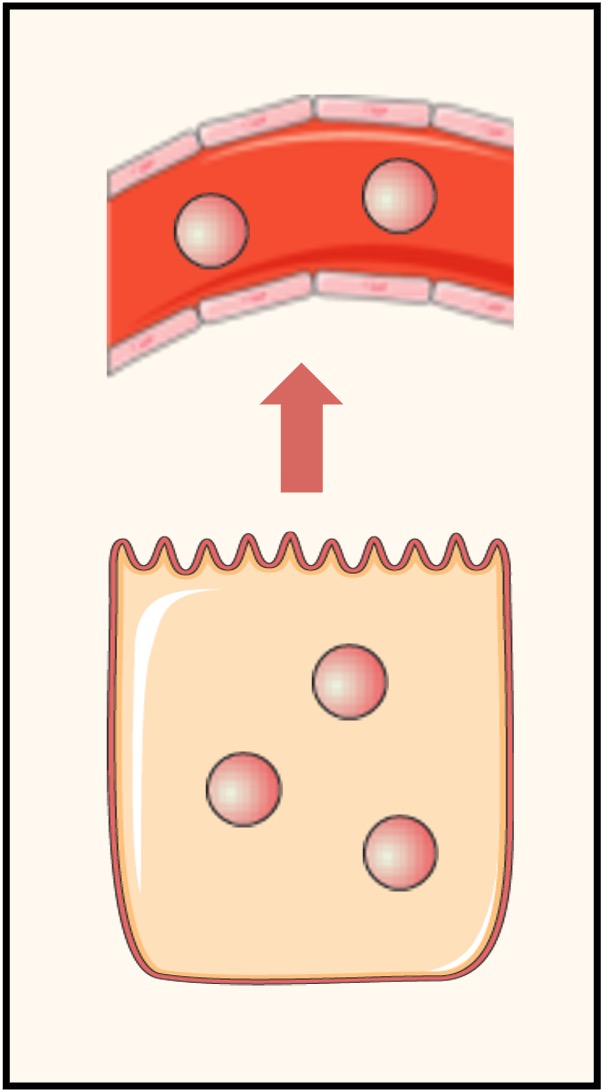
Paracrine
-
Paracrine signalling occurs when the chemicals released by a cell stimulate a neighbouring cell
-
An example is the stimulation of post-synaptic neurons by neurotransmitters released from a pre-synaptic neuron
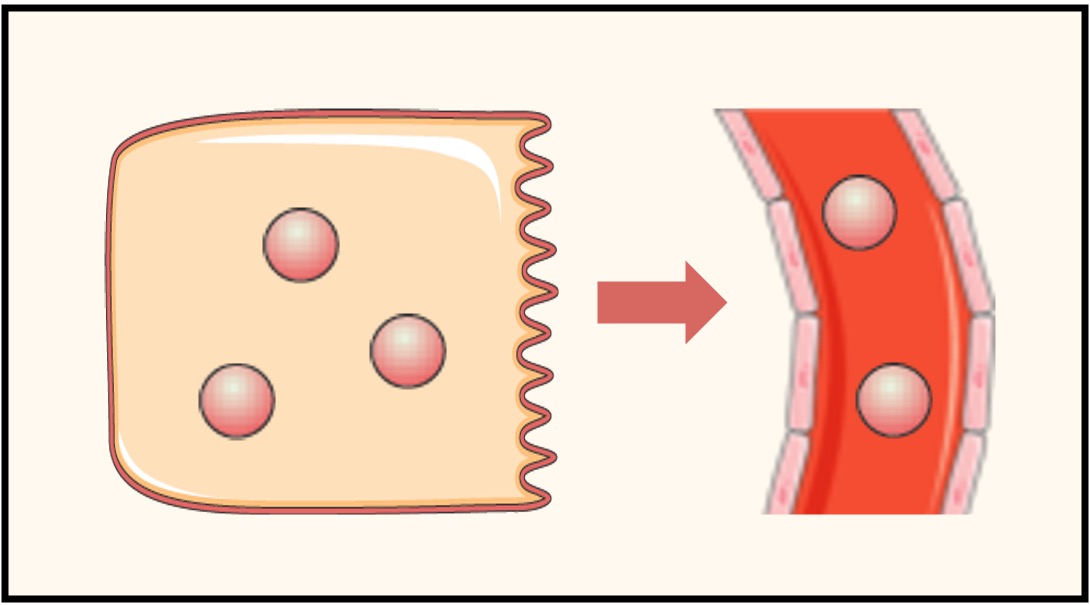
Endocrine
-
Endocrine signalling occurs when a chemical released by a cell travels in the bloodstream to activate distant cells
-
An example is the release of hormones from endocrine glands to activate distant target tissue
Signalling Types
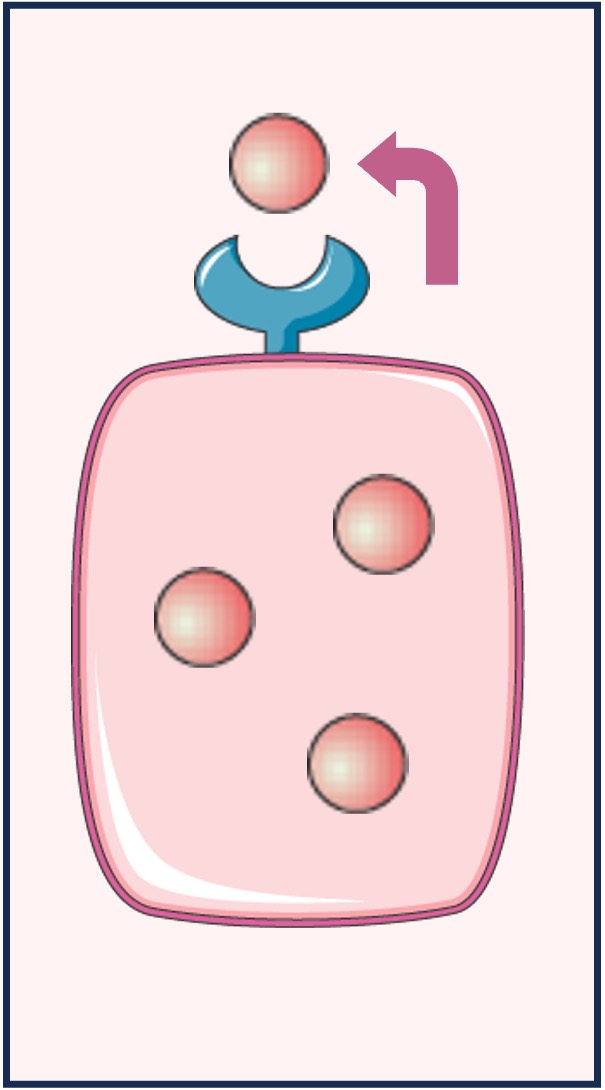
Autocrine
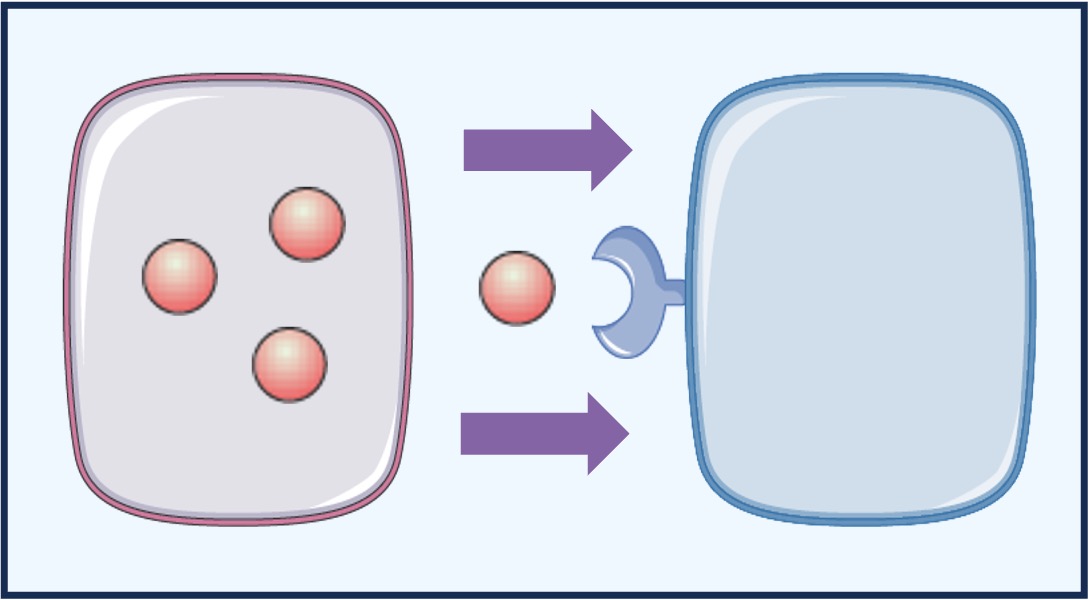
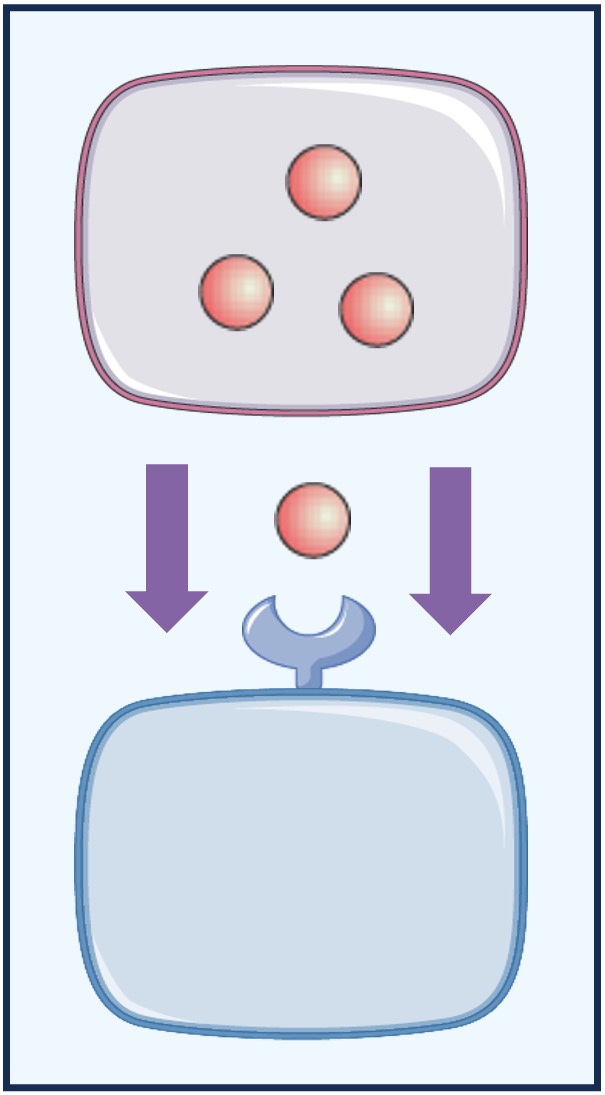
Paracrine