Taxonomic Ranks
Historically, biological classification schemes involved arranging organisms into groups (taxa) on the basis of shared characteristics
-
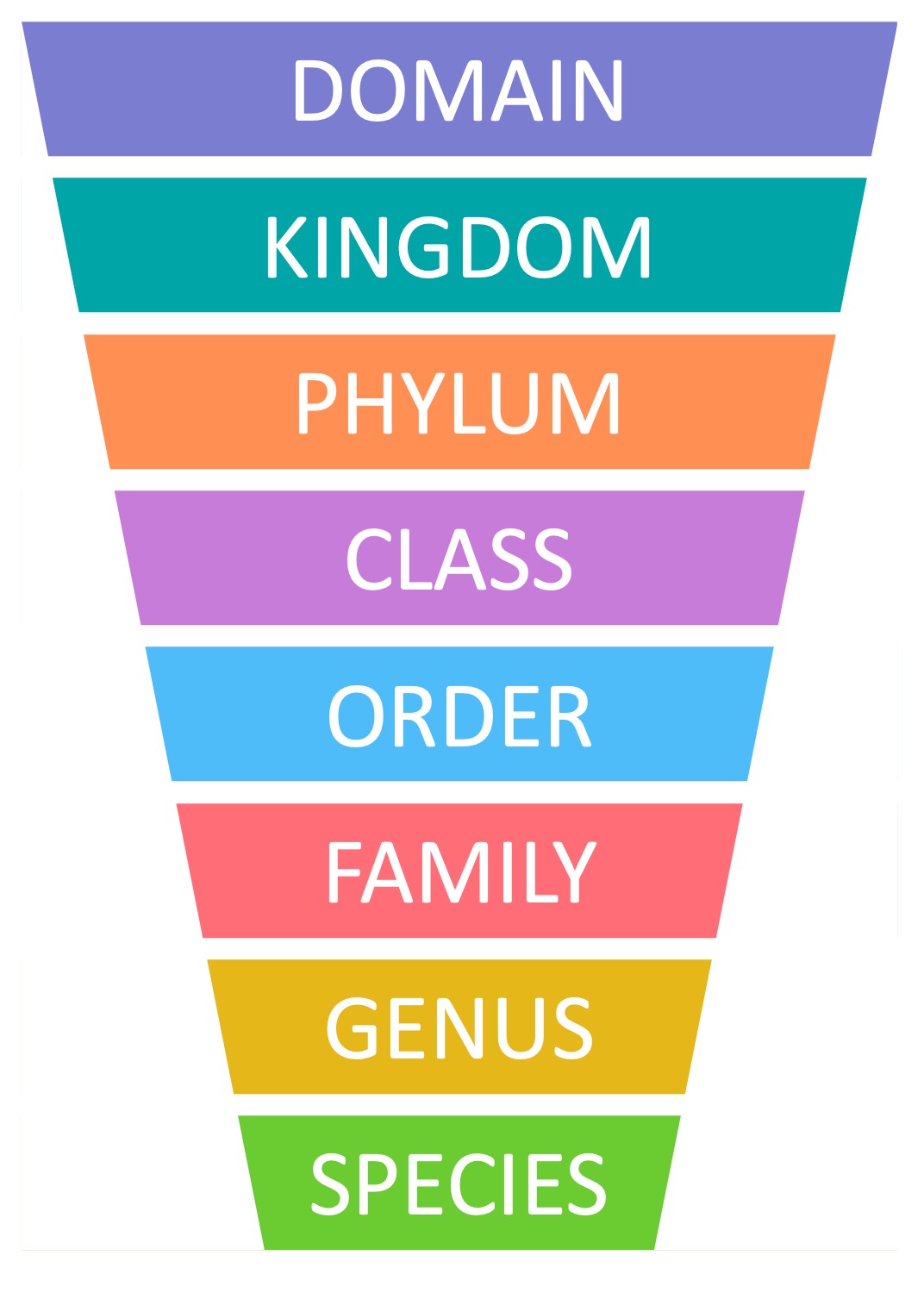
Taxa function as a series of hierarchical units – the more taxa organisms share, the more similar they are considered to be
-
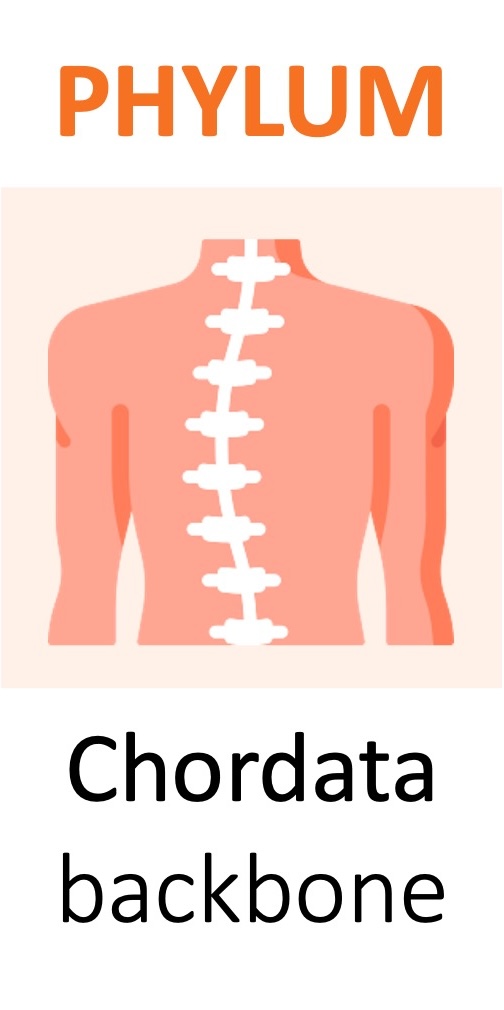
The taxa used are domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species (genus + species = scientific name)
There are many limitations involved with classifying organisms according to a hierarchy of taxa:
-
Taxonomic ranks set an arbitrary limit on the number of groupings by which an organism can be classified
-
Populations that are genetically diverging may be difficult to distinguish using limited taxonomic divisions (fixed rankings do not reflect the gradation of variation)
-
Organisms may share structural similarities due to convergent evolution (i.e. analogous structures) and may not actually be closely related
Hierarchy of Taxa