Target Effects
Transmembrane: Adrenaline
Adrenaline (epinephrine) is a water-soluble amine hormone released from the adrenal glands above the kidneys
-
Adrenaline coordinates a wide variety of cellular actions in response to threatening situations (‘fight or flight’ reactions)
Adrenaline cannot cross the plasma membrane and instead binds to transmembrane receptors on the cell surface
-
These transmembrane receptors are a type of G-protein coupled receptor and are found on a wide variety of cells (allowing for system wide responses)
-
The binding of the ligand causes an uncoupling of the G protein, which activates a membrane-bound enzyme called adenylate cyclase
-
This enzyme catalyses the conversion of ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP), which acts as a second messenger within the cell
-
Cyclic AMP may activate a variety of molecules within the cell (including protein tyrosine kinases), triggering a wide range of cellular responses
Fight or Flight Responses
Heart Rate

Contraction
Metabolism
Ventilation
Pupil Size
Intracellular: Sex Hormones
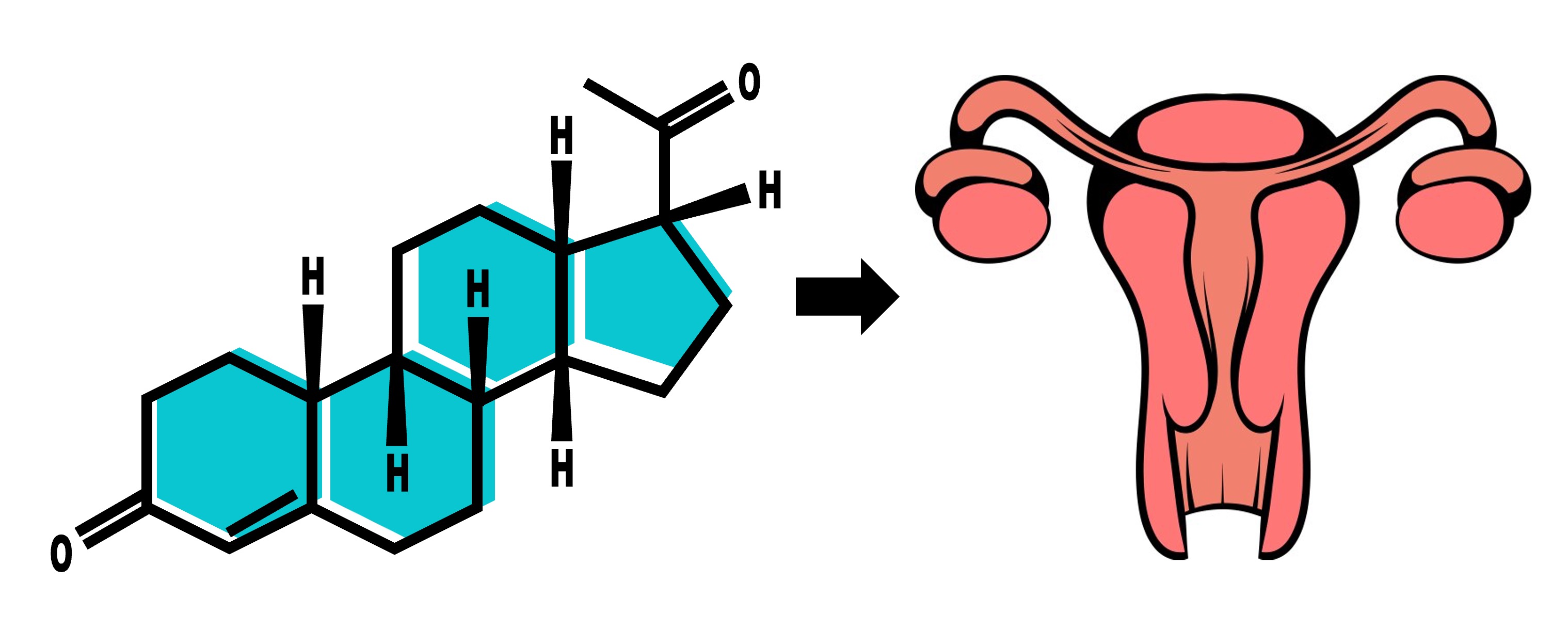
Estrogen (oestradiol) and progesterone are steroid hormones responsible for the development and regulation of female sex characteristics
-
These hormones are produced by the follicular cells within the ovary and are also secreted by the placenta during pregnancy
Oestradiol travels via the bloodstream and binds to intracellular receptors within the hypothalamus of the brain
-
The hormone-receptor complex functions as a transcription factor and regulates the expression of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
-
GnRH is released from the hypothalamus and acts on the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to stimulate the release of FSH and LH
-
FSH and LH are responsible for the control of the menstrual cycle and target cells found within the uterus
-
Oestradiol can either inhibit or promote the expression of GnRH, resulting in either a negative or positive feedback response
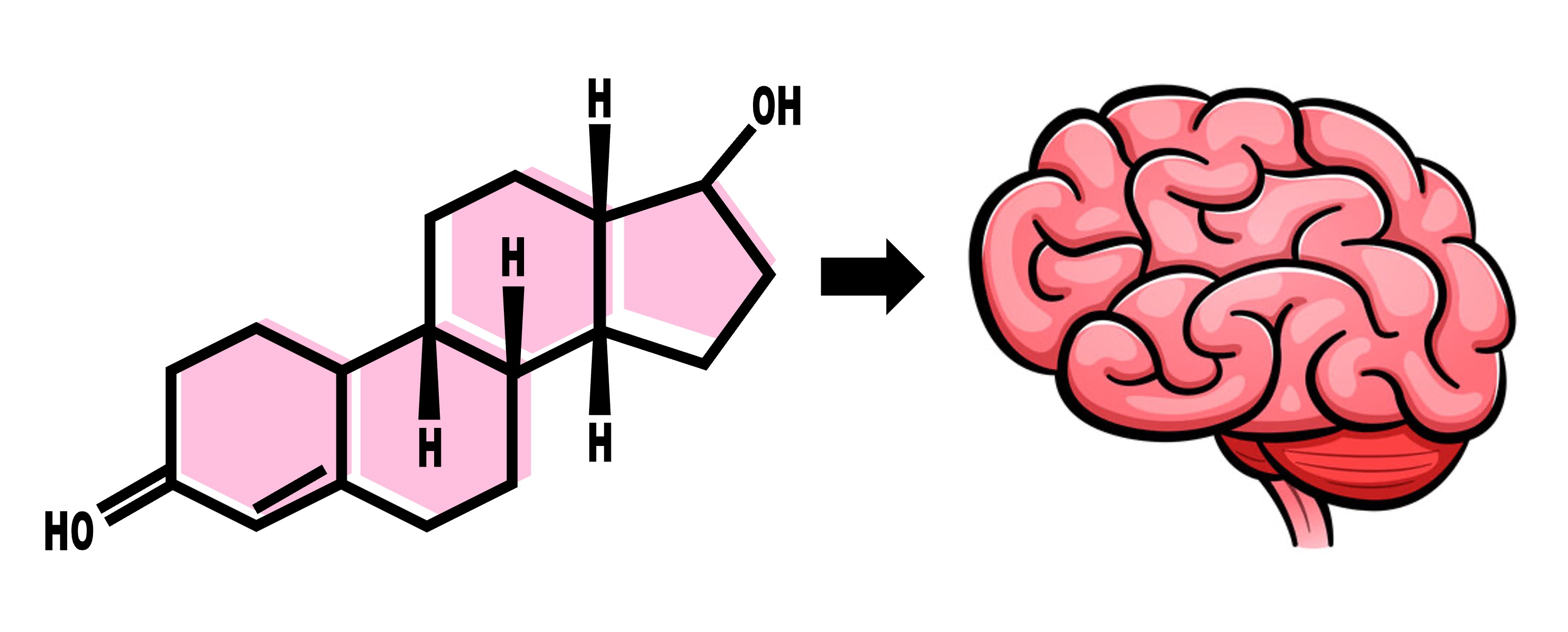
Progesterone binds to an intracellular receptor within the endometrial cells that form the uterine lining
-
The hormone-receptor complex functions as a transcription factor and regulates the expression of a growth factor
-
This growth factor promotes cell proliferation, leading to the thickening of the endometrial lining during the menstrual cycle and pregnancy