Signalling Molecules
A variety of signalling molecules (ligands) are involved in communicating messages between target cells and tissues
-
These signalling chemicals include hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines and calcium ions
Hormones
-
Hormones are chemical messengers that are released into the bloodstream by endocrine cells and act on distant target cells
-
Hormonal signals can persist for several hours after secretion and function to trigger changes in gene expression
-
Hormones can be hydrophilic (proteins and amines) or hydrophobic (steroids – transported bound to soluble proteins)
Neurotransmitters
-
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that are released by nerve cells and transmit signals across a synaptic cleft
-
These signals are rapid, with neurotransmitters being quickly removed from the synaptic gap after secretion
-
Neurotransmitters include amino acids, amines, peptides, esters and some gases
Cytokines
-
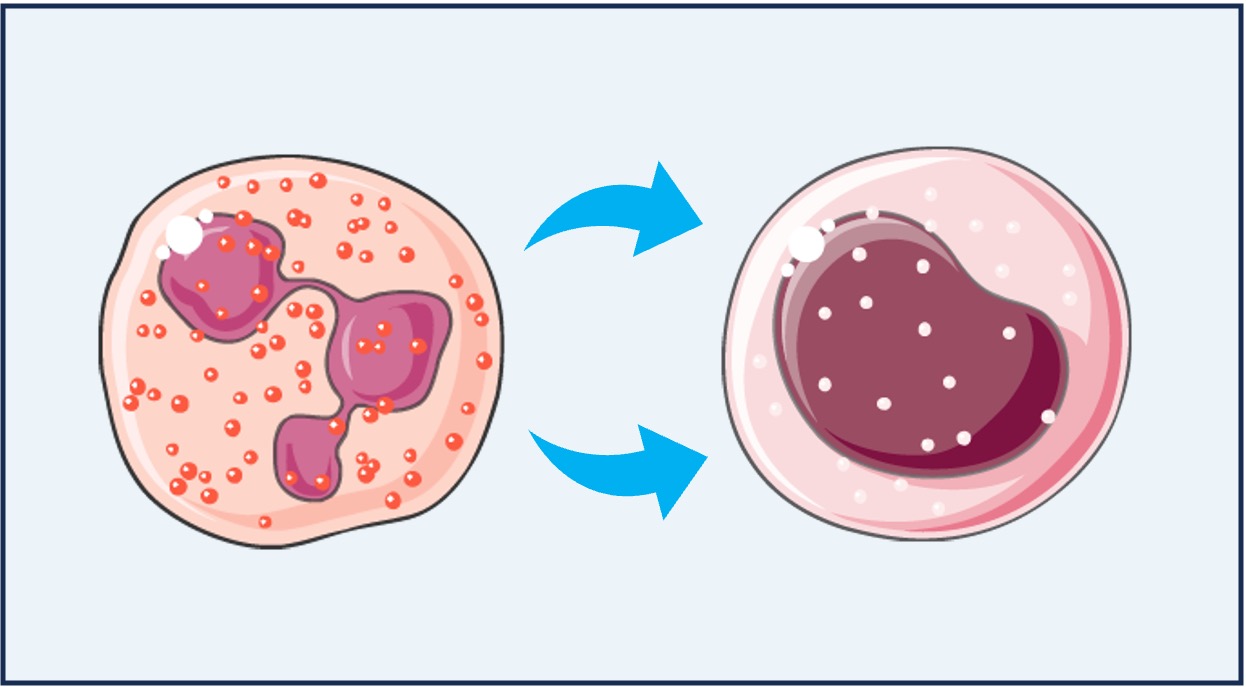
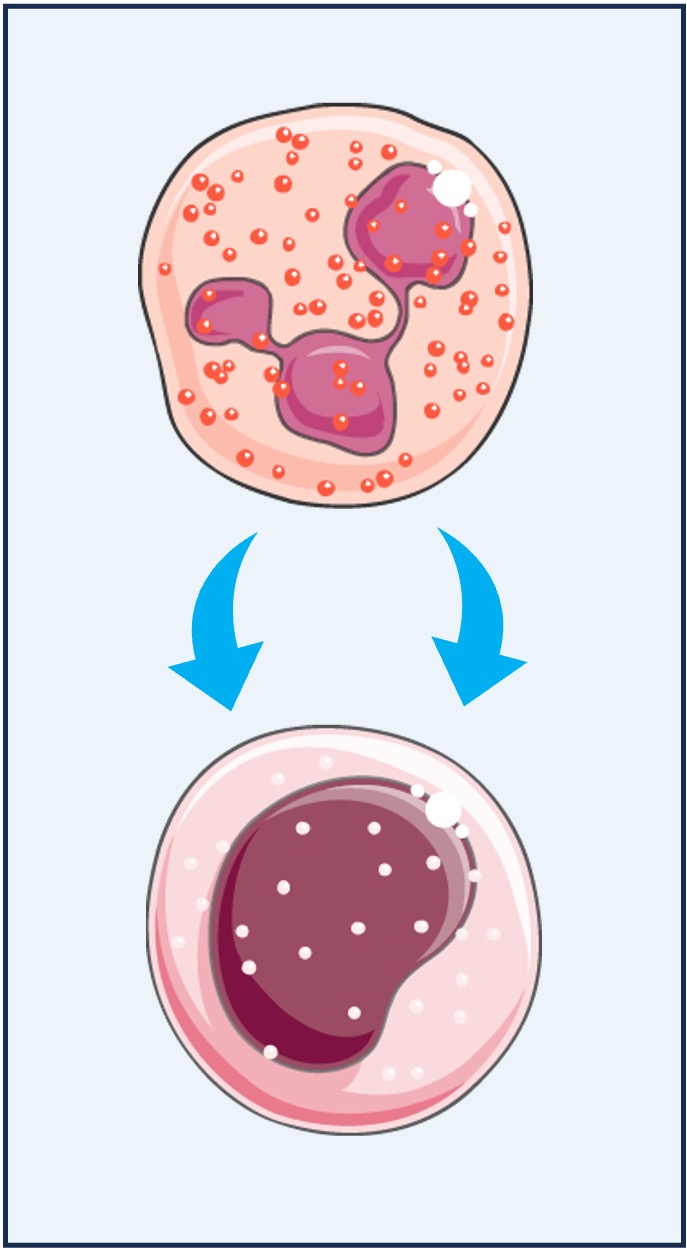
Cytokines are signalling proteins that are released by cells to regulate immune activity (i.e. immunomodulatory chemicals)
-
Cytokines are also involved in regulating the cell cycle (i.e. cell proliferation and embryonic development)
-
Examples of cytokines include interleukins, erythropoietin and interferon
Calcium Ions
-
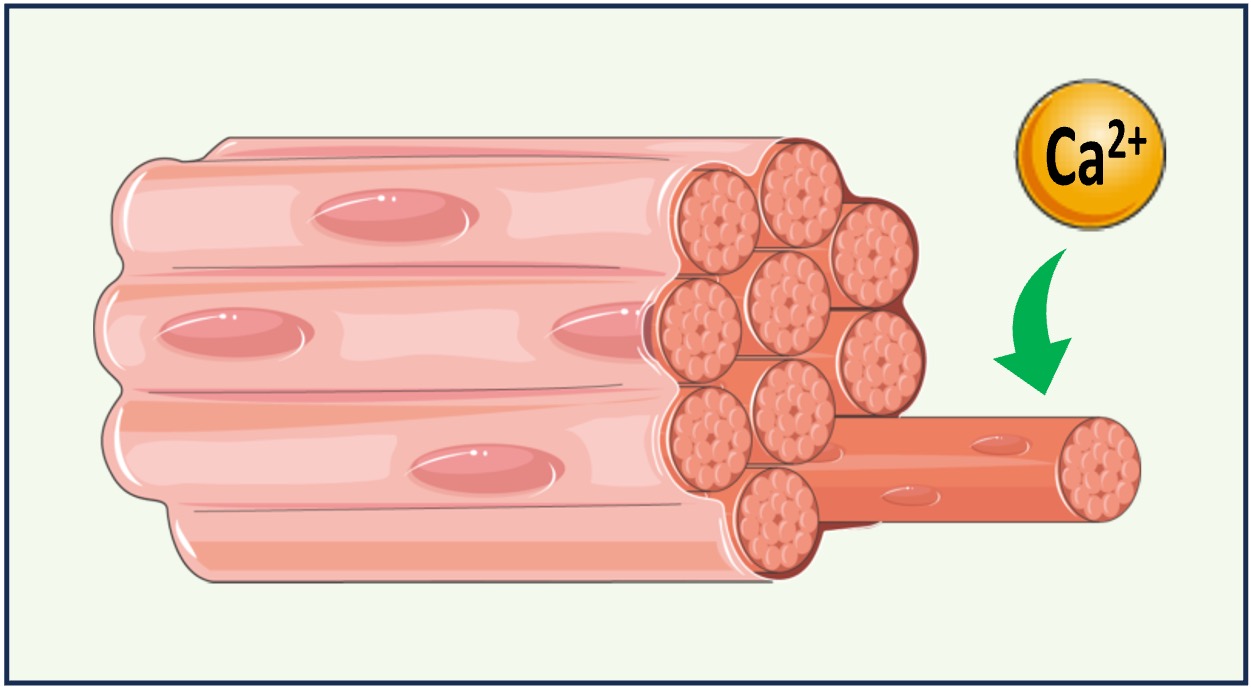
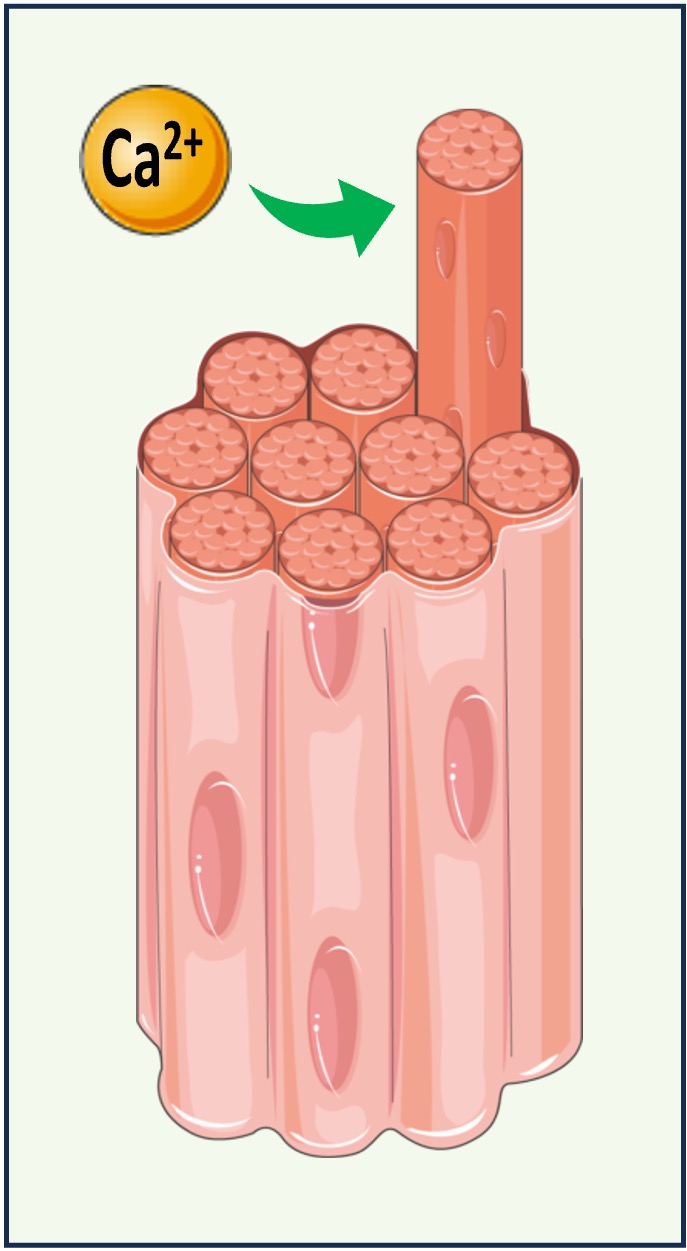
Calcium ions function as a common signalling chemical within cells (e.g. muscles and nerves)
-
Calcium is either transported into the cell via membrane proteins (active transport or facilitated diffusion) or released from internal compartments (e.g. sarcoplasmic reticulum)
-
Calcium ions can either trigger contraction (muscles), exocytosis (nerves) or act as second messengers
Signalling Chemicals
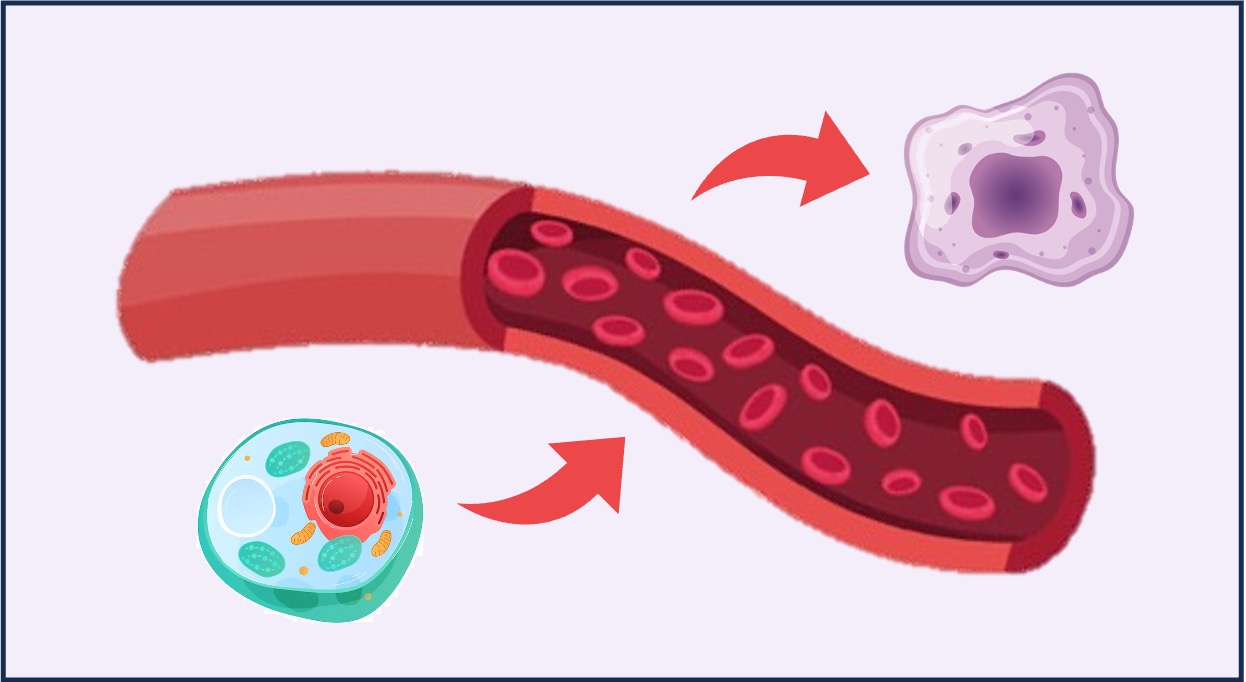

Hormone
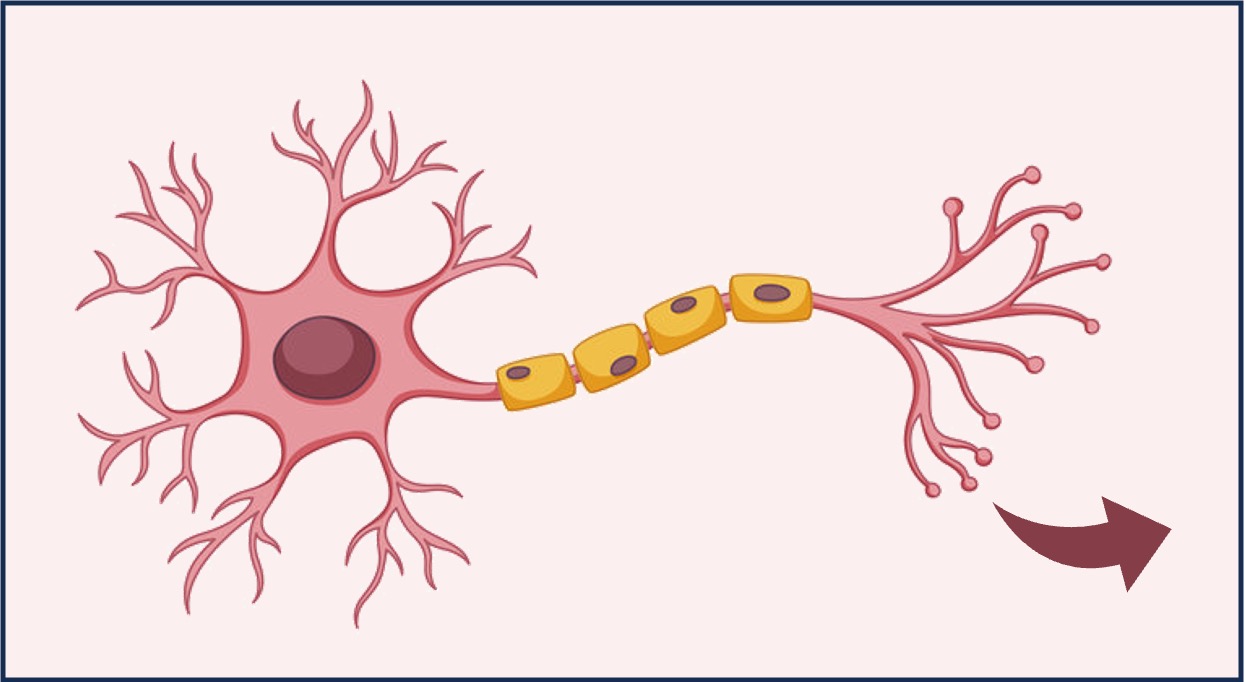
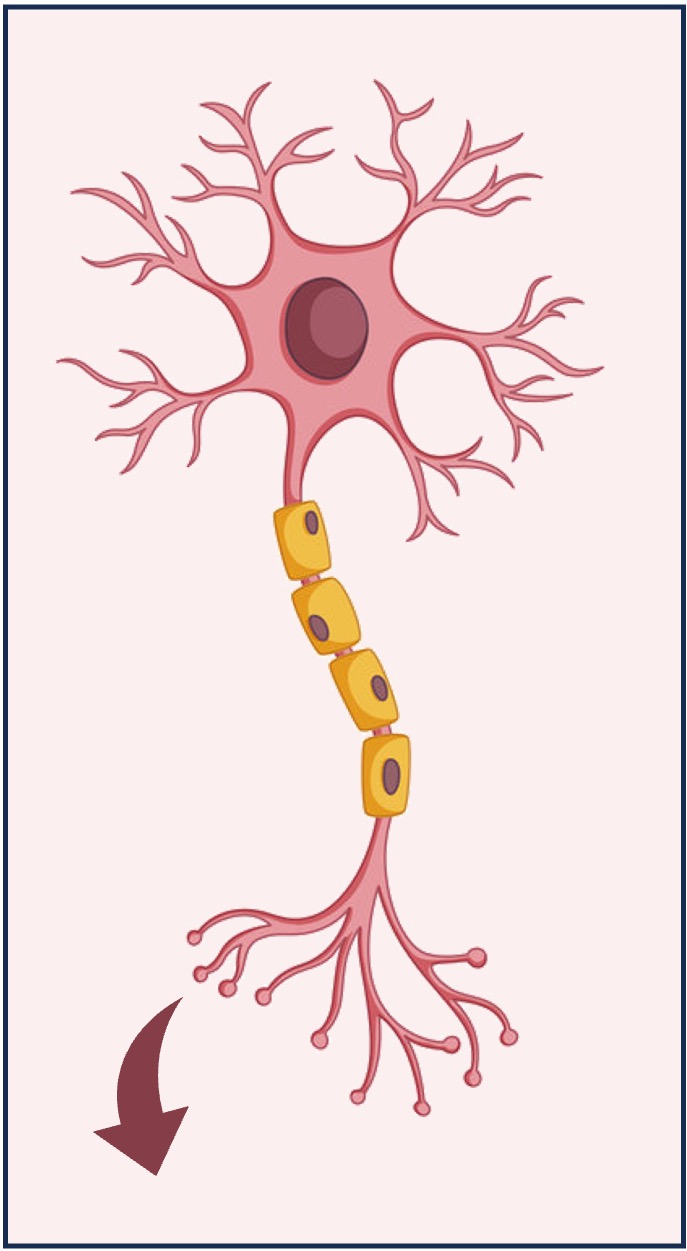
Neurotransmitter
Cytokine
Calcium Ion
Chemical Diversity
Hormones and neurotransmitters demonstrate different chemical structures according to the composition and location of their target receptor
-
These molecules must be complementary in shape and charge to their receptor and small and soluble to facilitate transit
Hormones
-
Amine hormones are synthesised by the modification of an amino acid and include melatonin (circadian rhythms) and adrenaline (heart rate)
-
Peptide hormones (< 50 amino acids) include antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin, while protein hormones (+50 amino acids) include insulin and glucagon
-
Steroid hormones are non-polar lipids derived from cholesterol and include the sex hormones (oestrogen and testosterone)
-
Amine
Peptide
Protein
Steroid
-
Melatonin
ADH
Insulin
Estrogen
-
Adrenaline
Oxytocin
Glucagon
Cortisol
Amine
Melatonin
Peptide
Oxytocin
Protein
Insulin
Steroid
Oestrogen
Neurotransmitters
-
Neurotransmitters can include small hydrophilic amino acids (glutamate, glycine) and amines (dopamine)
-
Larger neurotransmitters include peptides (endorphin) and esters (acetylcholine)
-
Certain gases can function as neurotransmitters (nitrous oxide), while some neurotransmitters also function as hormones (adrenaline)
-
Amine
Gas
Amino Acid
Peptide
-
Dopamine
Nitrous oxide
Glutamate
Endorphin