Signal Pathways
Membrane Potentials
Neurotransmitters can trigger changes to the membrane potential of a cell by binding to ligand-gated ion channels
-
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that is used throughout the nervous system and binds to cholinergic transmembrane receptors
Acetylcholine is essential for muscle contraction and is also involved in several nervous pathways within the brain (including memory, arousal and learning)
-
In response to a nerve impulse, acetylcholine is released by presynaptic neurons into the synaptic cleft
-
The neurotransmitter binds to ligand-gated ion channels on the postsynaptic cell and trigger a conformational change in the channel protein
-
This causes the ion channel to open, allowing sodium ions to passively diffuse into the cell and trigger depolarisation
-
This change in membrane potential may trigger the opening of voltage-gated ion channels, facilitating the propagation of a nerve impulse
-
Acetylcholine molecules are then broken down to prevent continued stimulation and the products are recycled by the presynaptic neuron
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
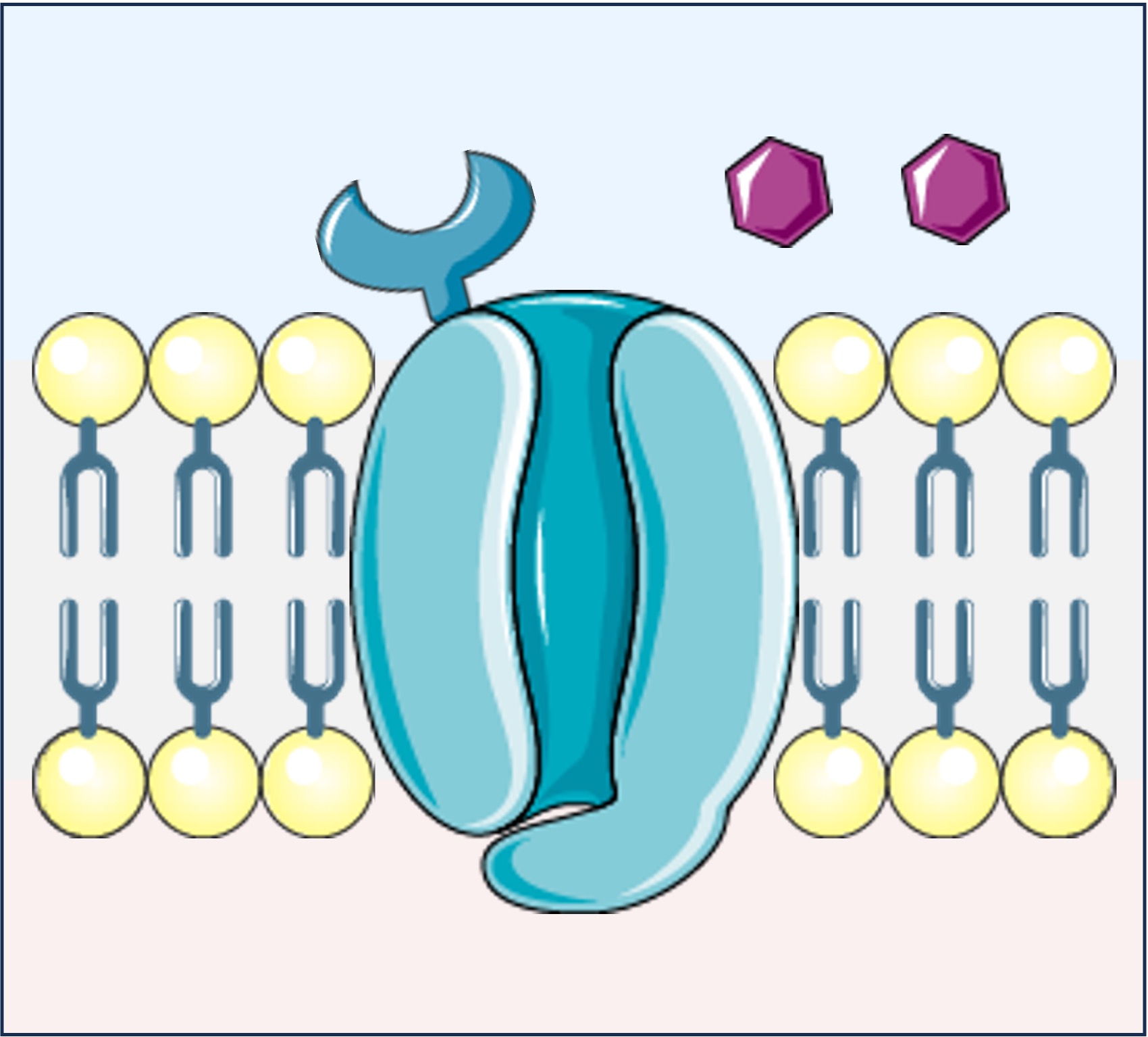
Inactive Channel (Closed)
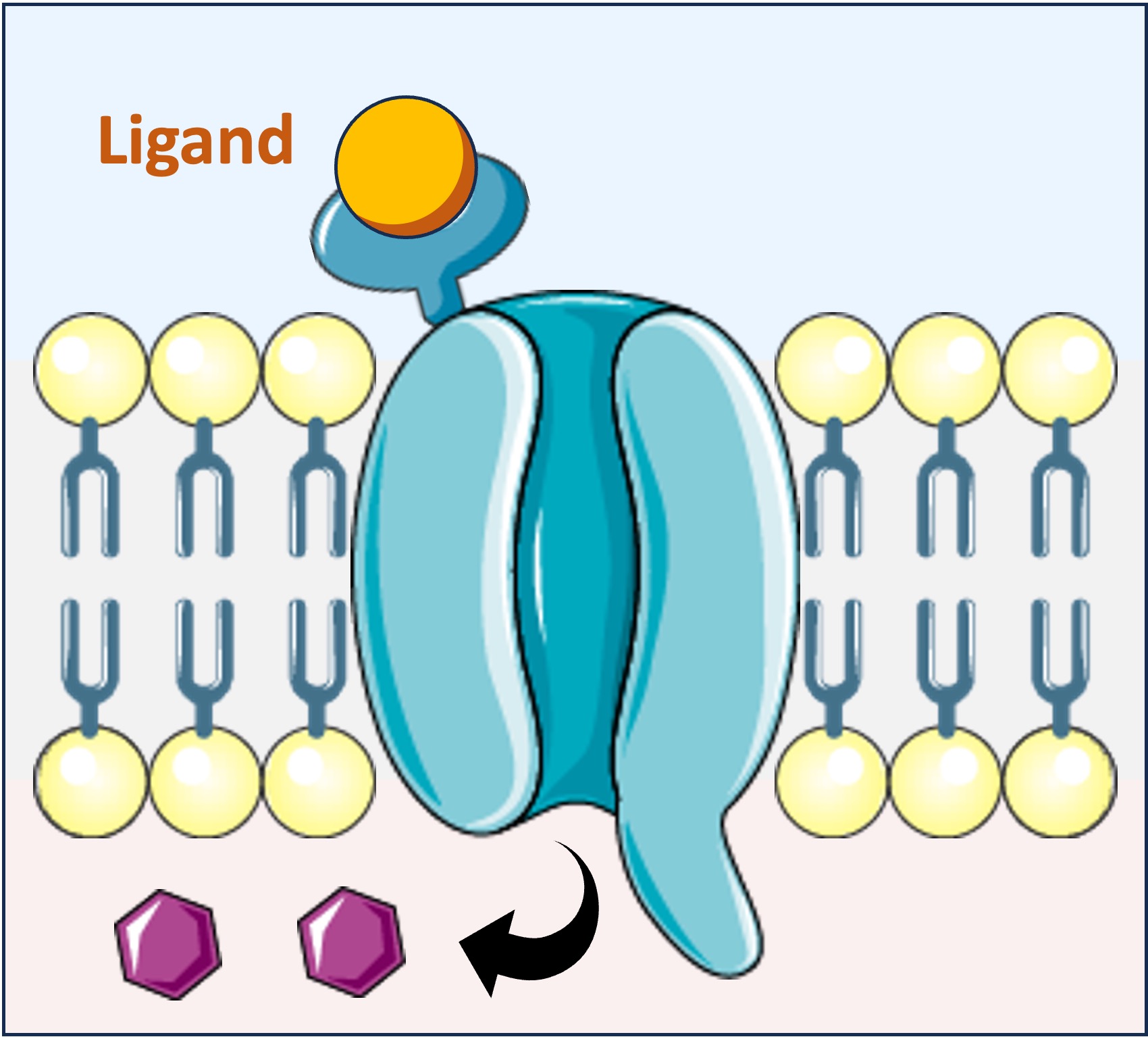
Activated Channel (Open)
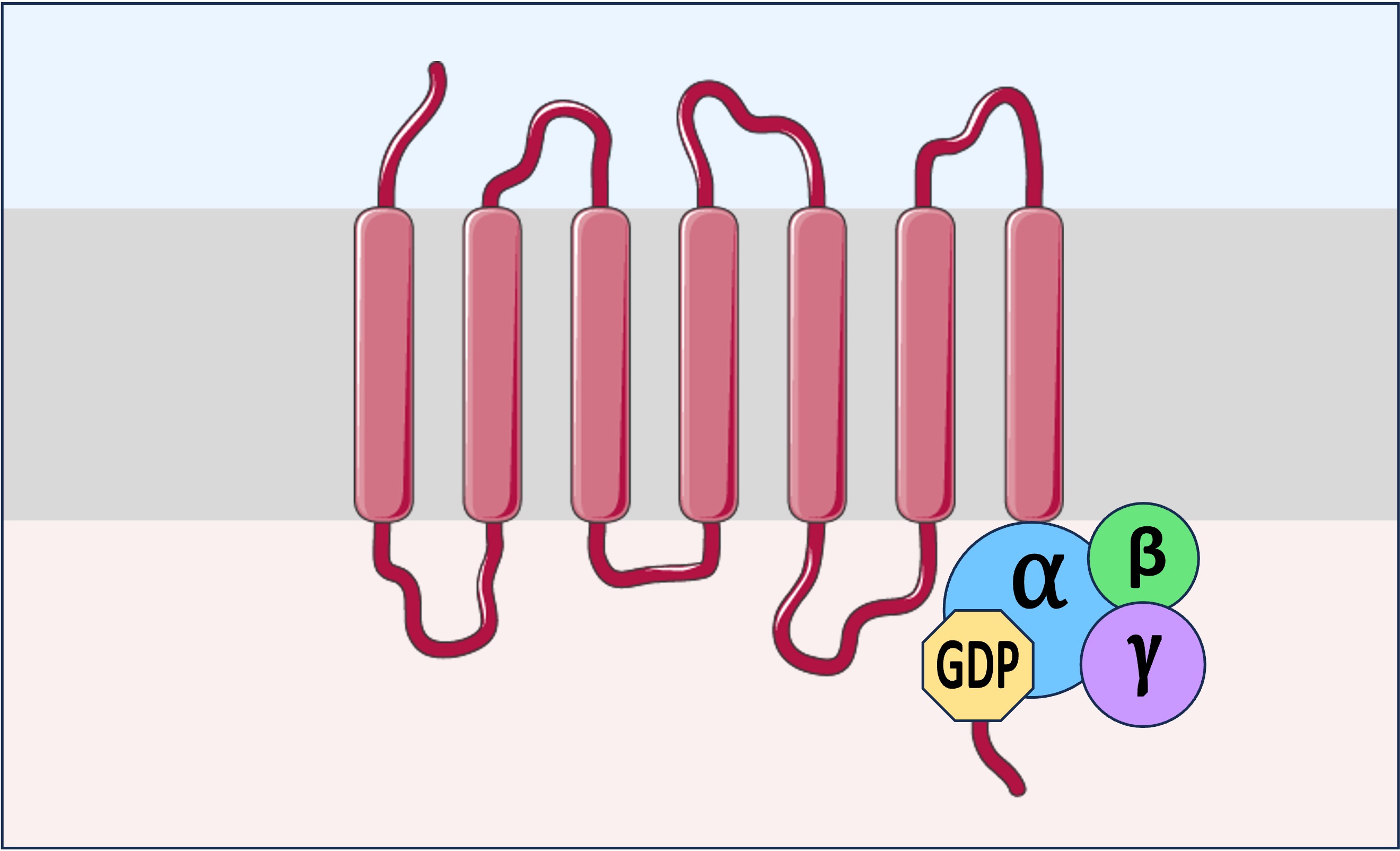
G-Proteins
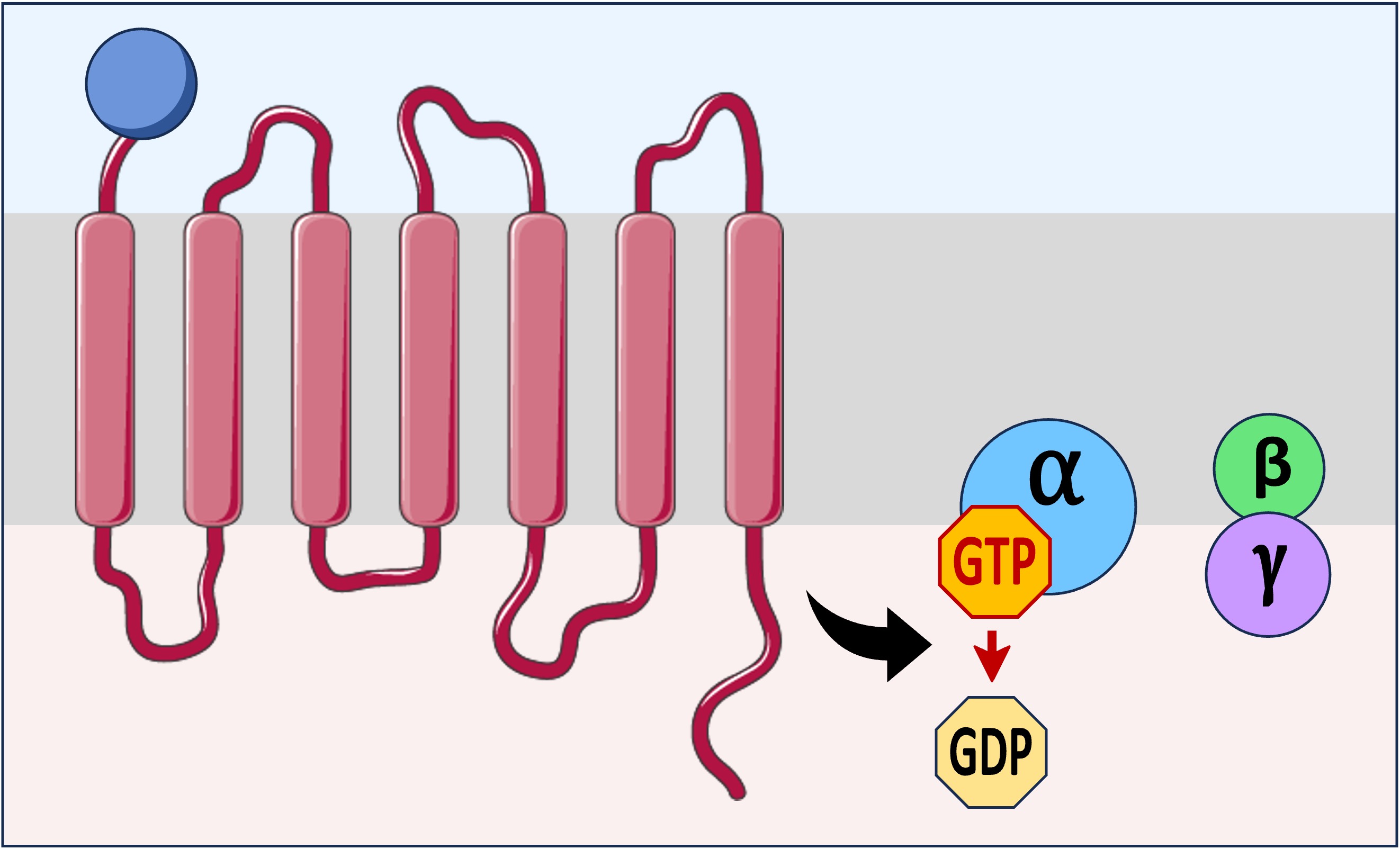
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) consist of a single polypeptide embedded within the plasma membrane
-
The extracellular portions of the GPCR form a binding site for the ligand, while the intracellular portions attach to the G-protein
All G-proteins consist of a complex of three subunits – an alpha subunit bound to GDP and a beta-gamma dimer
-
When the ligand binds to the receptor, the G-protein becomes activated and the GDP detaches from the alpha subunit
-
A molecule of GTP replaces the GDP, which causes the alpha subunit and beta-gamma dimer to dissociate from the receptor
-
Both components can diffuse laterally along the membrane and interact with other membrane proteins or second messenger molecules
G-Protein Coupled Receptors
Inactive Receptor (Coupled)
Active Receptor (Decoupled)
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
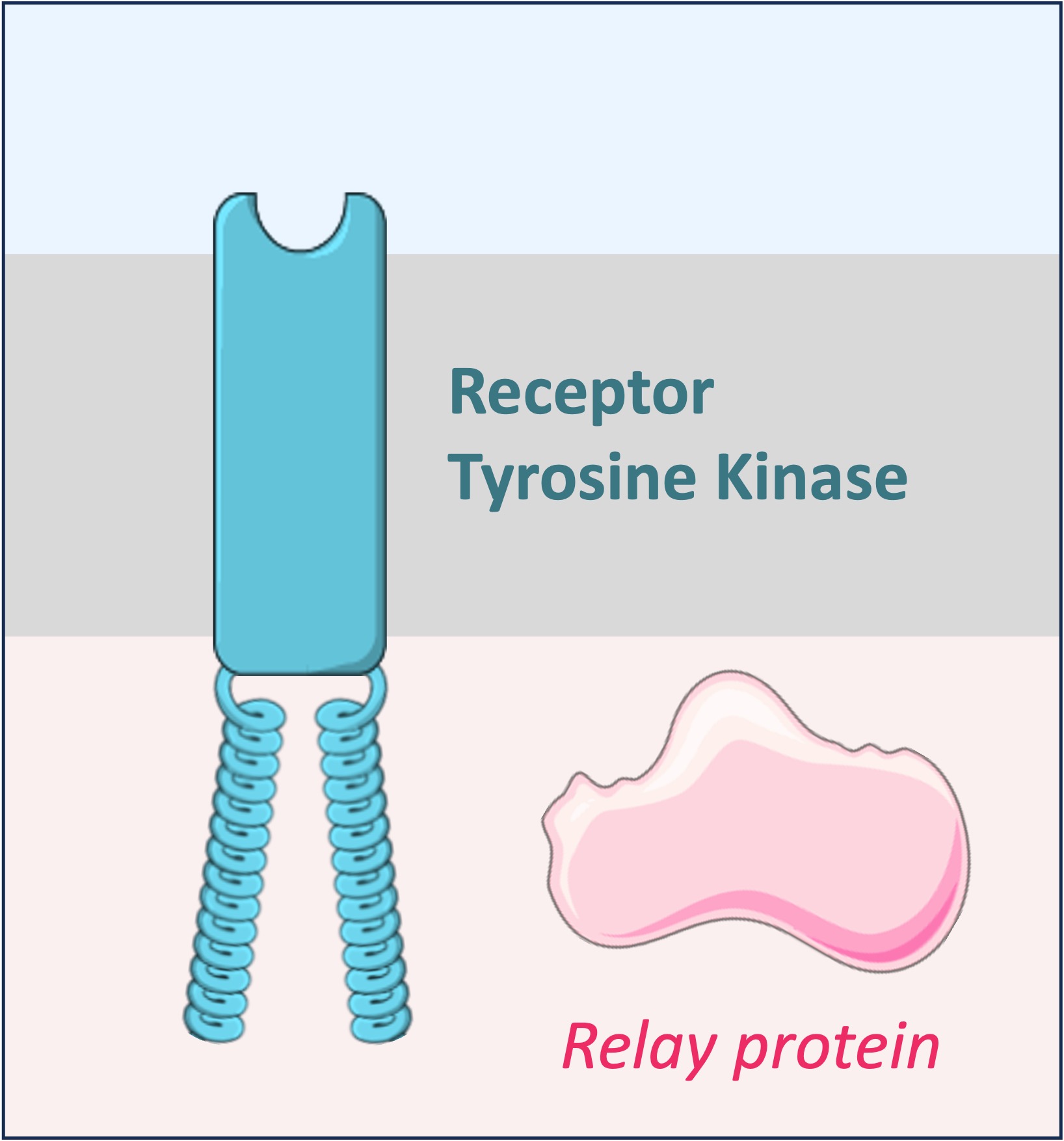
Receptor tyrosine kinases are transmembrane enzymes that catalyse the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on proteins
-
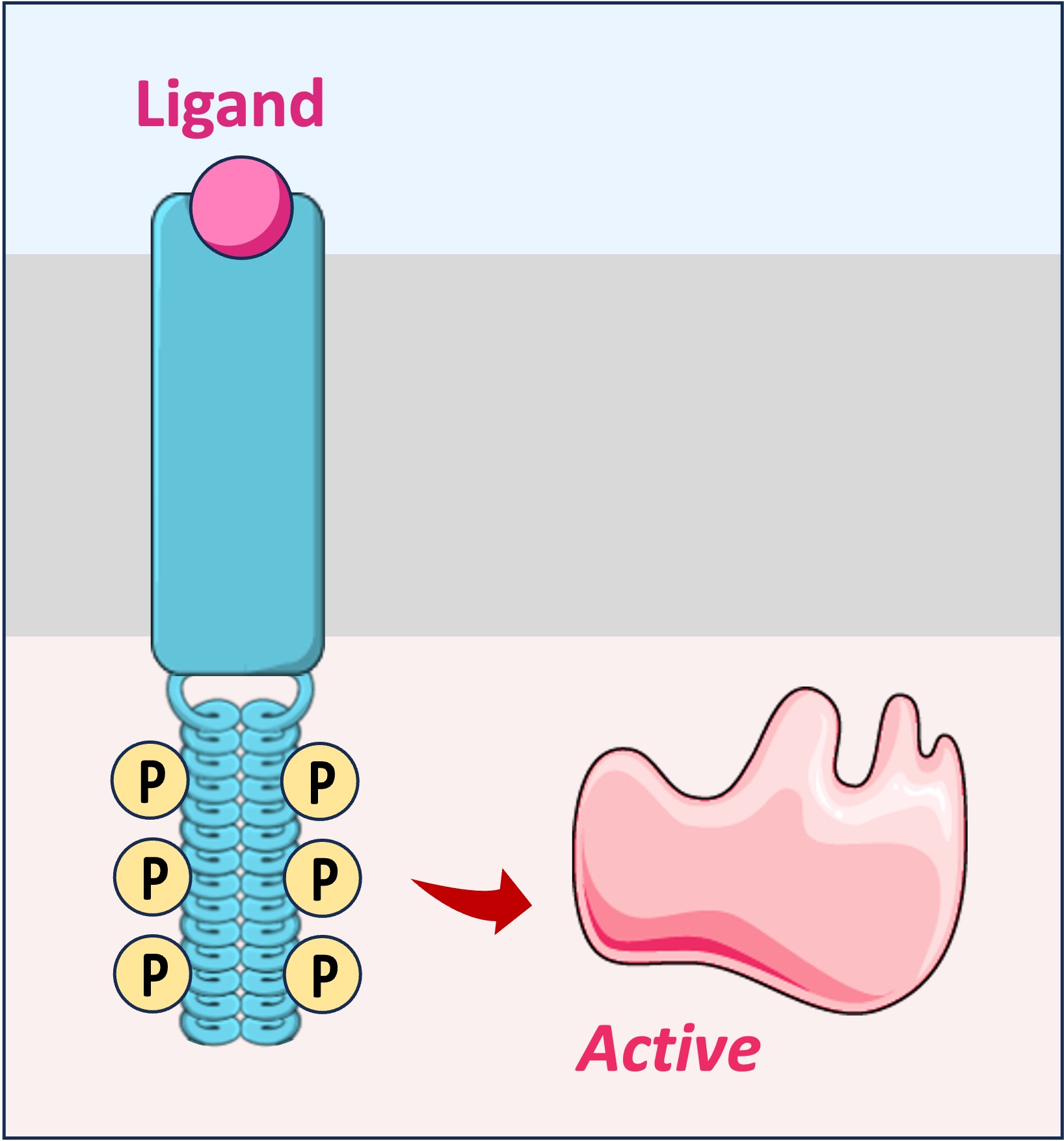
The phosphorylation is achieved using phosphate groups from ATP and causes a change in shape and activity within the modified protein
The insulin receptor is an example of a receptor tyrosine kinase that functions to trigger an uptake of glucose within target cells
-
The insulin receptor possesses two intracellular tails that become connected upon insulin binding
-
Each tail phosphorylates various tyrosine residues on the other tail, facilitating the recruitment of relay proteins
-
These relay proteins act as second messengers and activate a variety of different signal transduction pathways
-
One cellular response is the movement of vesicles embedded with glucose transporters to the plasma membrane – this results in the increased uptake of glucose
Insulin Receptor
Inactive Receptor
Active (Phosphorylated)
Gene Expression
Intracellular receptors are used for signalling pathways involving hydrophobic ligands that can freely cross the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane
-
The ligand and receptor form an activated complex within either the cytoplasm or nucleus and functions as a transcription factor
-
The complex binds to DNA and mediates the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter region of a gene
-
This causes a temporary change in gene expression that results in a change in cellular activity
Steroid hormones are hydrophobic ligands and are transported within the bloodstream bound to soluble transport proteins
-
Testosterone is a hormone involved in the development of male sex characteristics and promoting muscle growth
-
Estrogen (oestradiol) is involved in the development of female sex characteristics and regulating the menstrual cycle
-
Progesterone is involved in pregnancy – it prepares the uterine lining for implantation and coordinates milk production by the mammary glands
Estrogen Receptor
Receptor (Alpha Subunit)