Placenta
The placenta develops during pregnancy and functions as the life support system for the foetus
-
It facilitates the exchange of materials between the mother and foetus and it secretes hormones to maintain pregnancy after the corpus luteum has degenerated
-
By completing these actions, the placenta allows the foetus to be retained in the uterus to a later stage of development than in mammals that do not develop a placenta
Structure of the Placenta
-
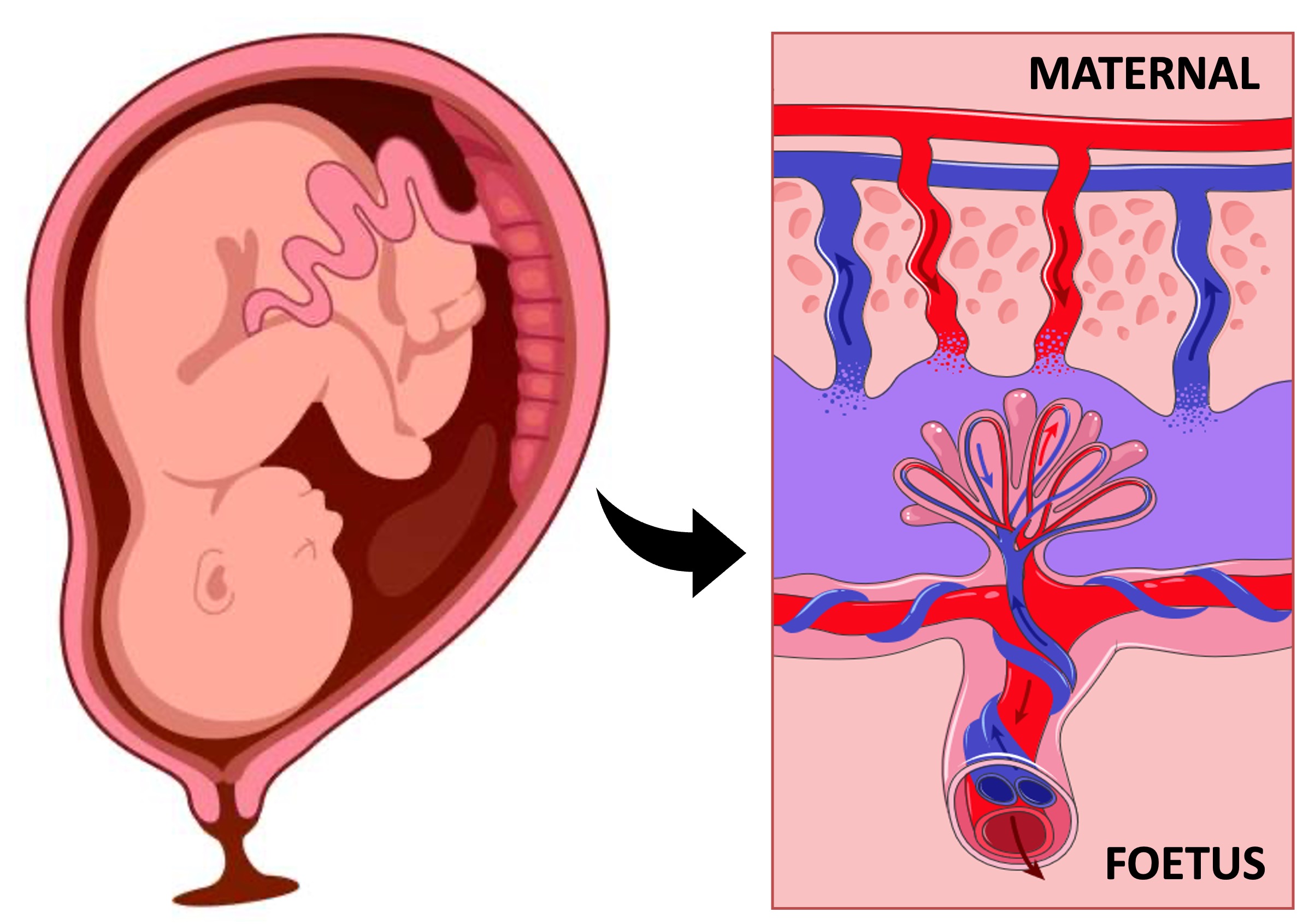
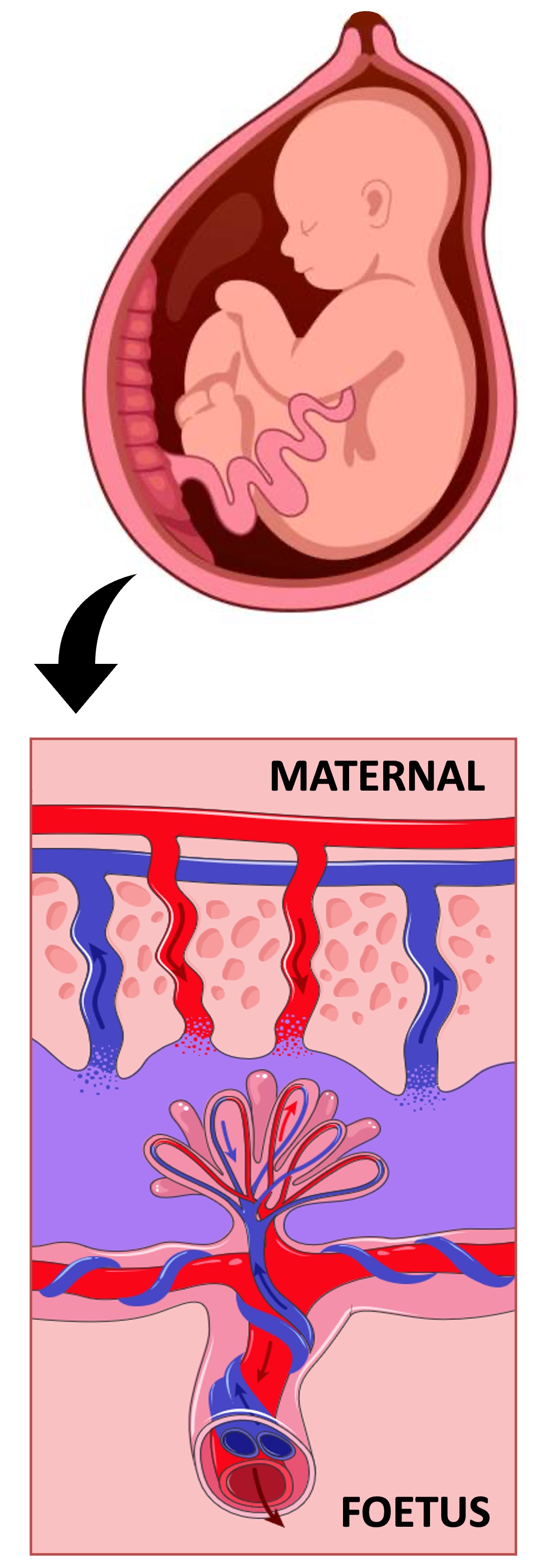
The placenta is a disc-shaped structure that is composed of a combination of maternal and foetal tissues
-
Maternal blood pools from open-ended arterioles into intervillous cavities within the placenta called lacunae
-
Chorionic villi from the foetus extend into these pools of blood and mediate the exchange of materials between the foetus and the mother
-
Exchanged material is transported from the villi to the foetus via an umbilical cord, which connects the foetus to the placenta
-
Upon birth, the placenta is expelled from the uterus with the infant – it is then separated from the infant by severing the umbilical cord (the point of separation becomes the belly button)
Material Exchange
-
The chorionic villi from the foetus is bathed in maternal blood and acts as a site of material exchange between the mother and the foetus
-
Chorionic villi are lined by microvilli to significantly increase the available surface area for material exchange
-
Materials such as oxygen, nutrients, vitamins, antibodies and water will diffuse from the maternal blood into the foetal capillaries
-
Foetal waste (such as carbon dioxide, urea and hormones) will diffuse from the chorionic villi into the maternal blood vessels
Placenta Structure