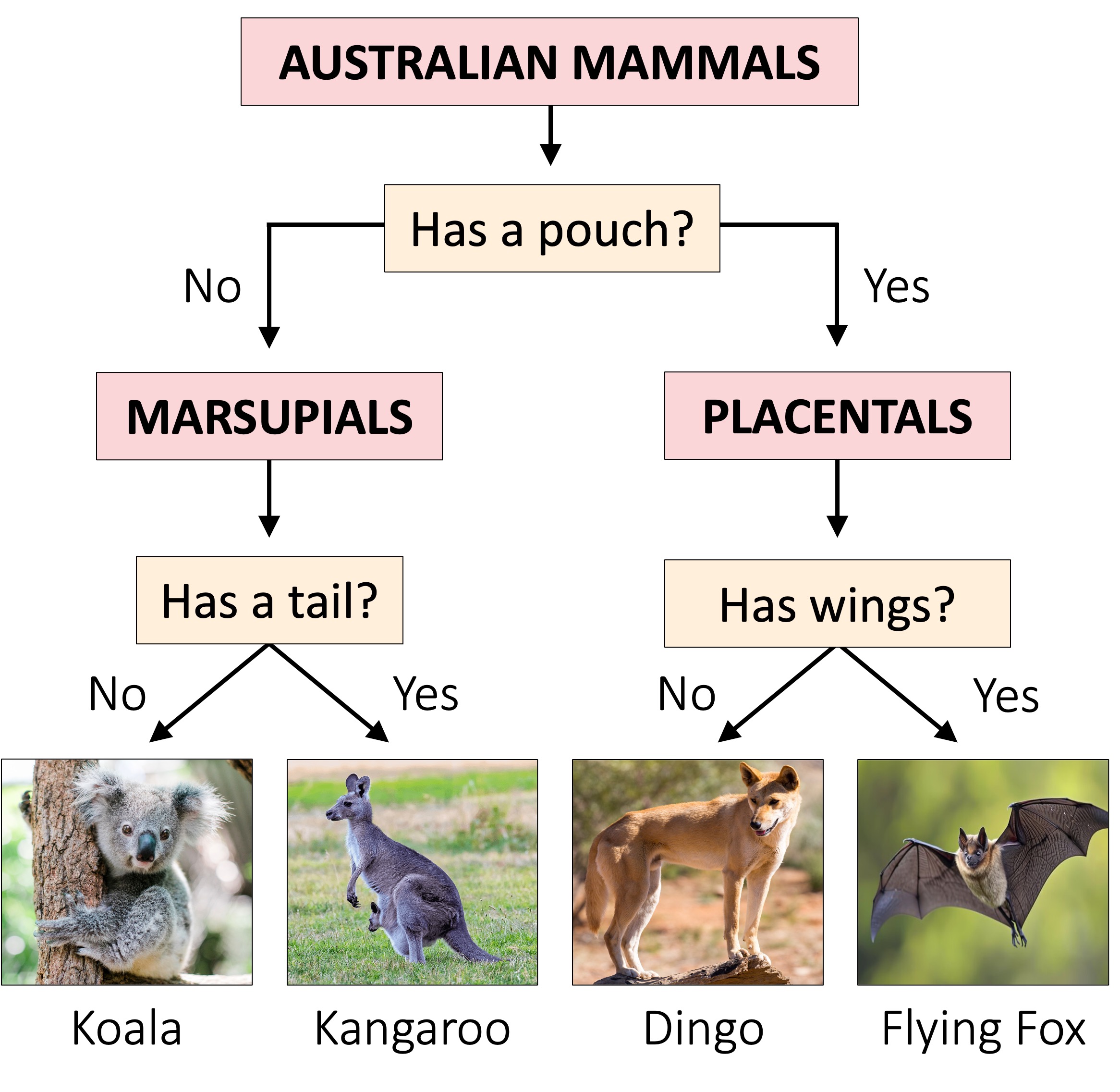
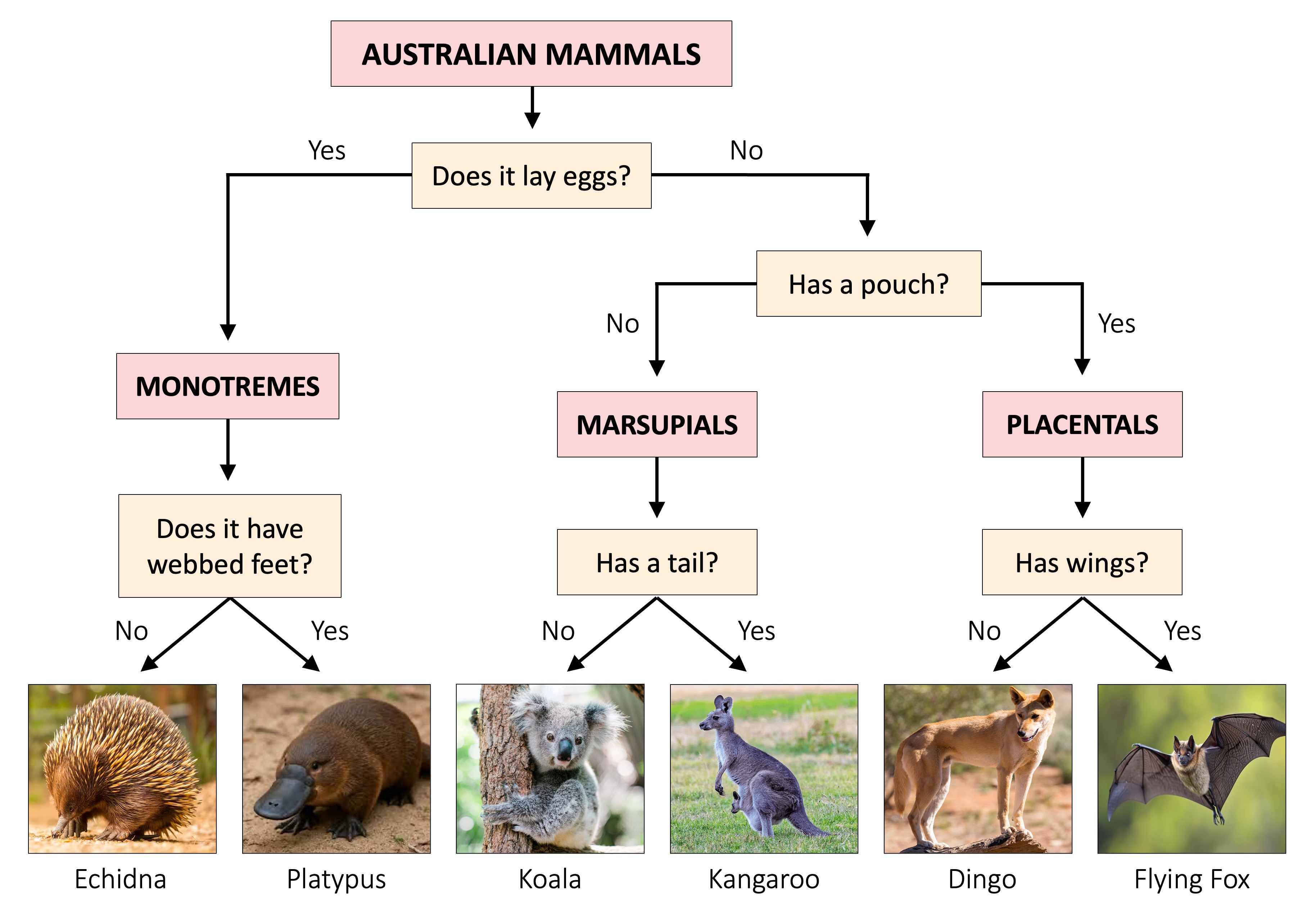
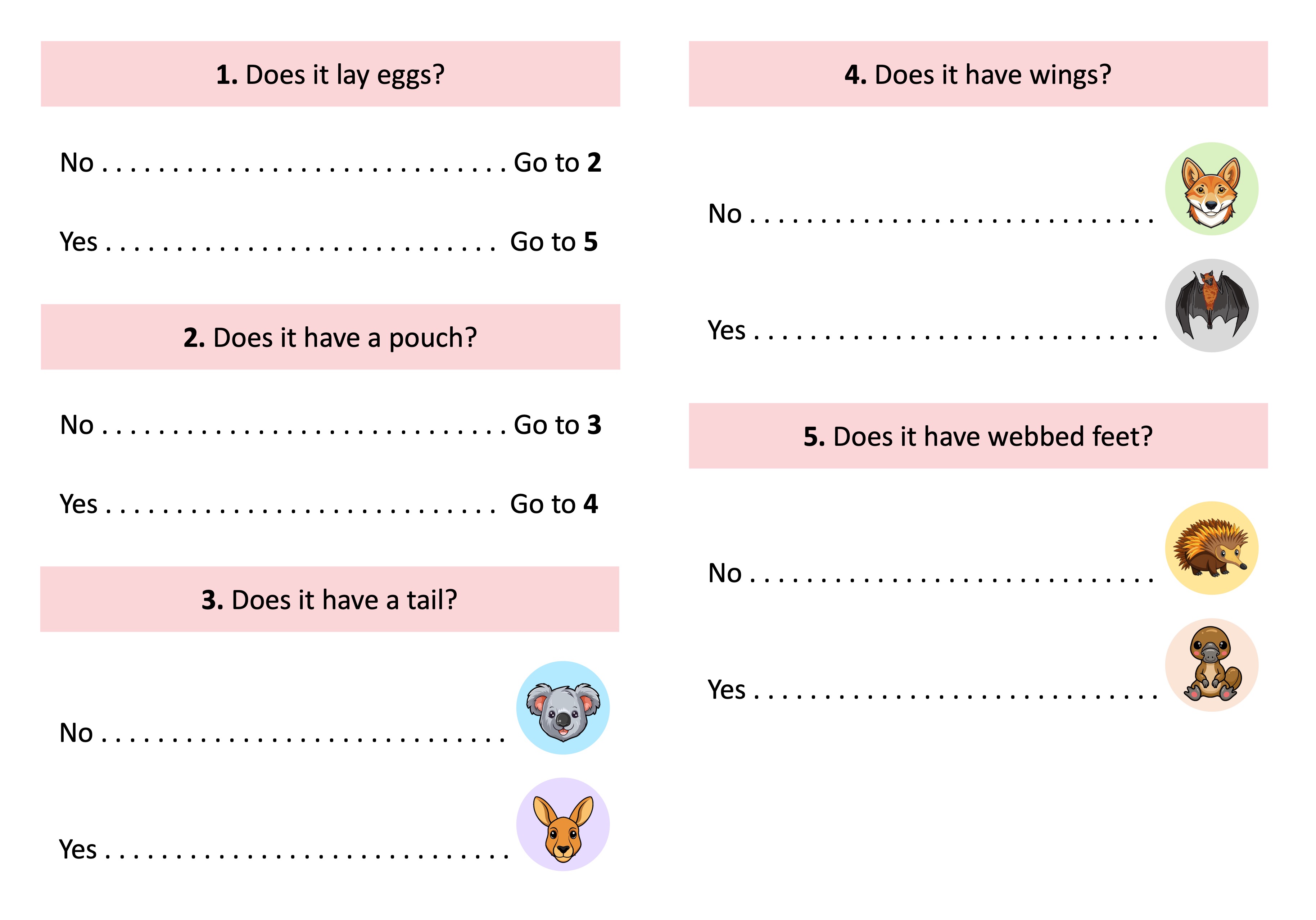
Dichotomous Keys
A dichotomous key is a method of identification whereby groups of organisms are divided into two categories repeatedly
-
With each sequential division, more information is revealed about the specific features of a particular organism
-
When the organism no longer shares its totality of selected characteristics with any other organism, it has been identified
When using a dichotomous key to identify specimens it is preferable to use immutable features (i.e. features that do not change)
-
Size, colouration and behavioural patterns may all vary amongst individuals and across lifetimes
-
Physical structures (e.g number of limbs) and biological processes (e.g. reproduction methods) make for better characteristics
Dichotomous keys are usually represented in one of two ways:
-
As a branching flowchart (diagrammatic representation)
-
As a series of paired statements laid out in a numbered sequence (descriptive representation)
Dichotomous Key