Cladograms
Cladistics is a method of classifying organisms into groups of species called clades (from Greek ‘klados' = branch)
-
Each clade consists of an ancestral organism and all of its evolutionary descendants
-
Members of a clade will possess common characteristics as a result of their shared evolutionary lineage
Clades can be organised according to branching diagrams (cladograms) in order to show evolutionary relationships
-
Assessments are less subjective and unlikely to result in misclassifications (such as incorrectly classifying based on analogous structures)
-
Molecular sequences provide the most objective evidence for placing organisms in a clade, however morphological traits can also be used
Examples of Clades
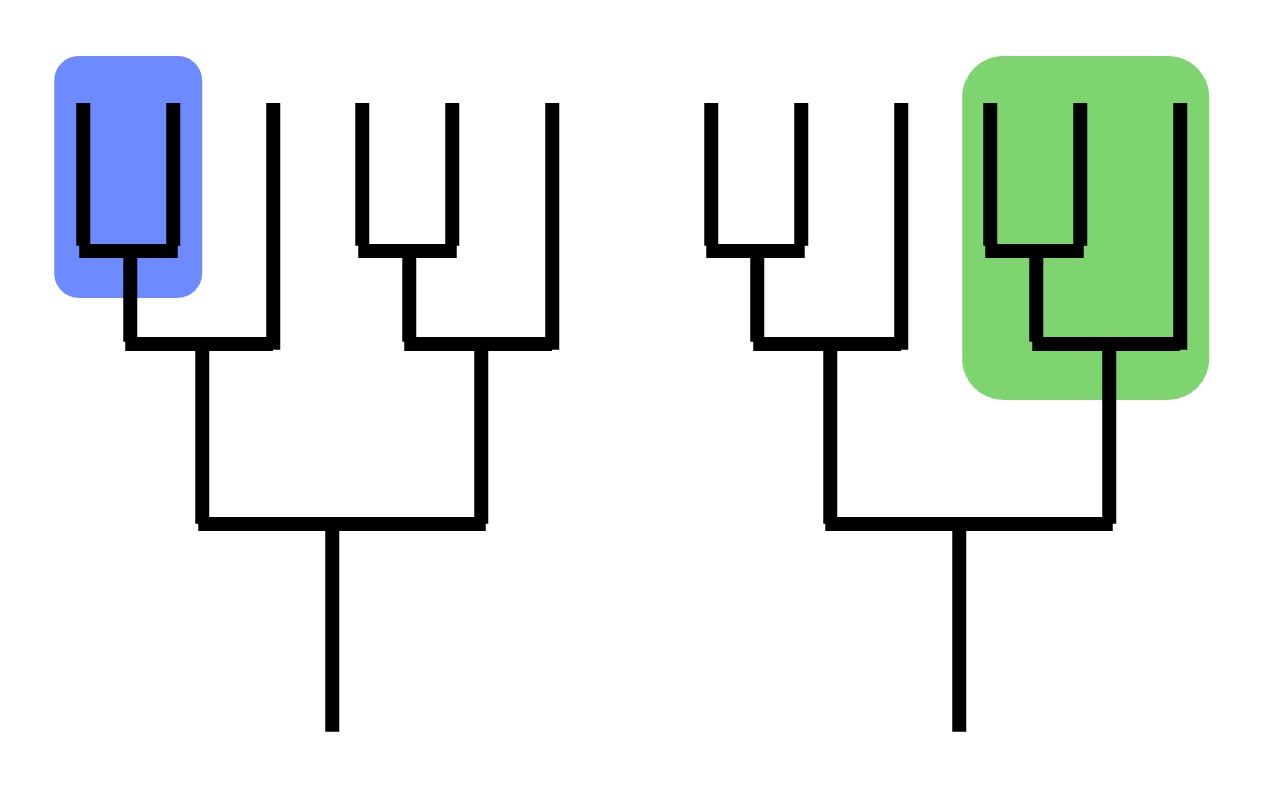
Clades
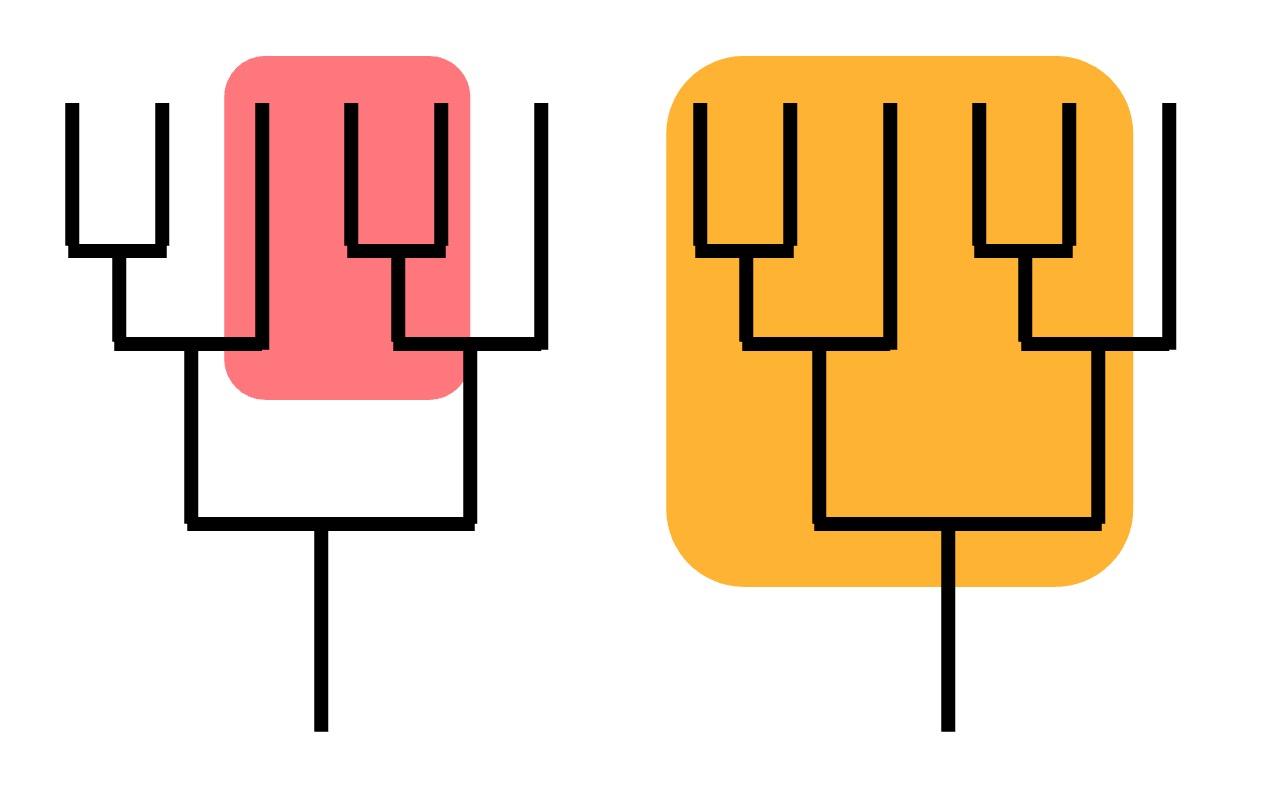
Not Clades
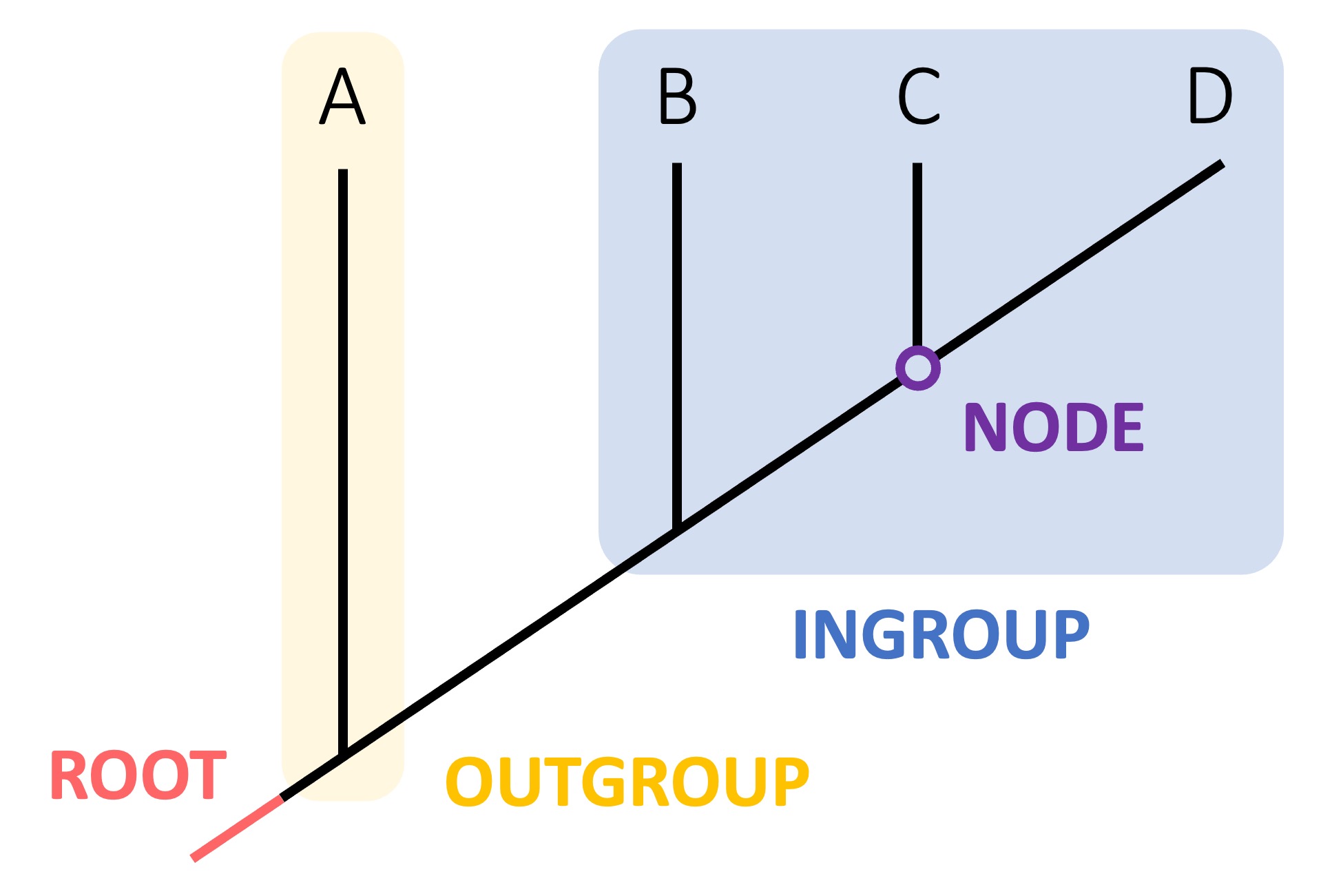
Cladograms
Cladograms are tree diagrams that are used to show evolutionary relationships between species
-
Nodes: A node is a branch point in the cladogram that represents a point of divergence from a common ancestor (e.g. speciation)
-
Root: The root is the starting point from which all branches extends and represents the most recent common ancestor of all the organisms in the diagram
-
Outgroup: The outgroup is the species that is most distantly related to all other species and functions as a reference point
Cladograms show the probable sequence of divergence and hence demonstrate the likely evolutionary history of a clade
-
The fewer the number of nodes between two groups the more closely related they are expected to be
Cladograms