Cancers
Tumours are abnormal cell growths resulting from uncontrolled cell division and can occur in any tissue or organ
-
Diseases caused by the growth of tumours are collectively known as cancers
Tumours are caused by mutations to the genes that control the cell cycle
-
Mutations may be caused by proofreading errors that may occur during DNA replication (in the S phase of interphase)
-
Mutations may also be caused by external agents called mutagens (a cancer-causing mutagen is called a carcinogen)
-
Physical mutagens include sources of radiation – such as X-rays and ultraviolet (UV) light
-
Chemical mutagens may include reactive oxygen species and certain metals (e.g. arsenic)
-
Biological agents include certain viruses, bacteria or mobile genetic elements (transposons)
-
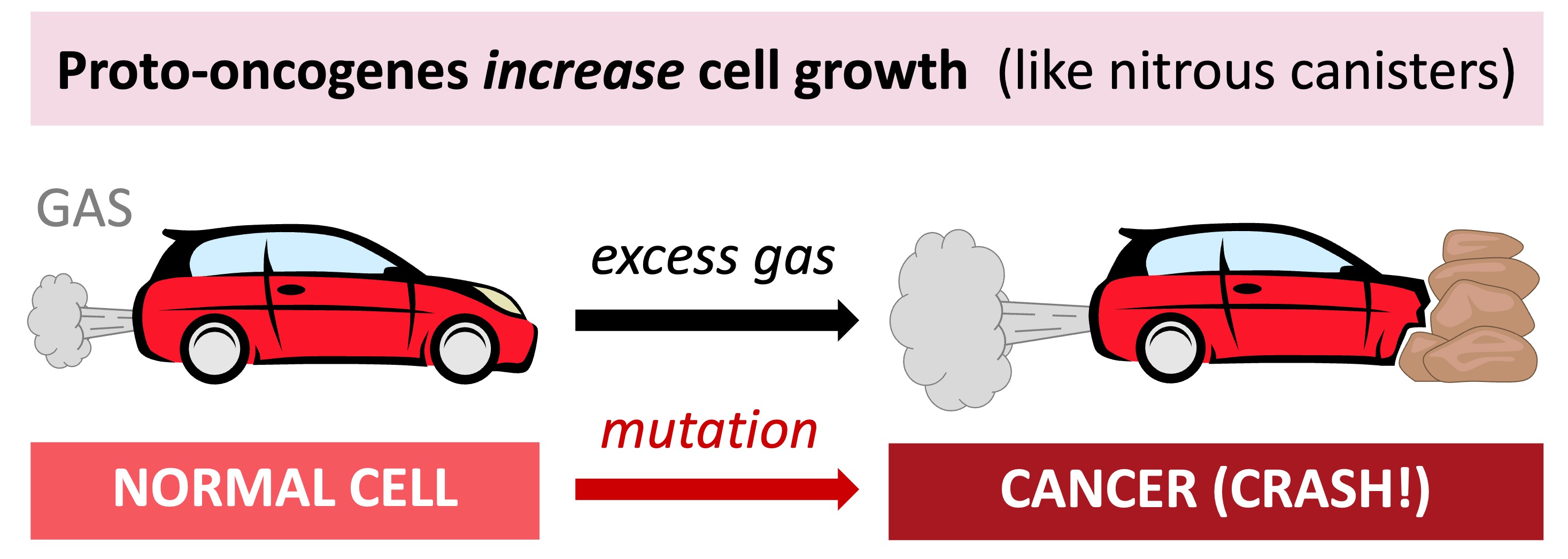
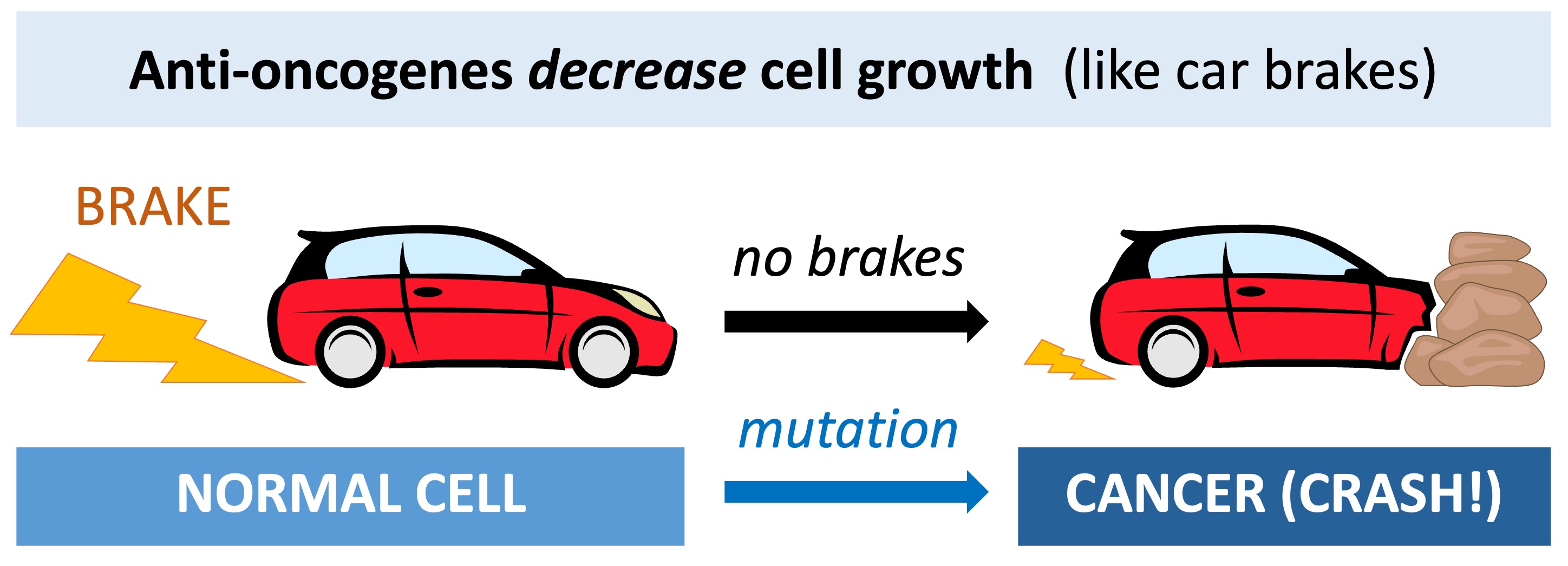
Most cancers are caused by mutations to two basic classes of genes – proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes
-
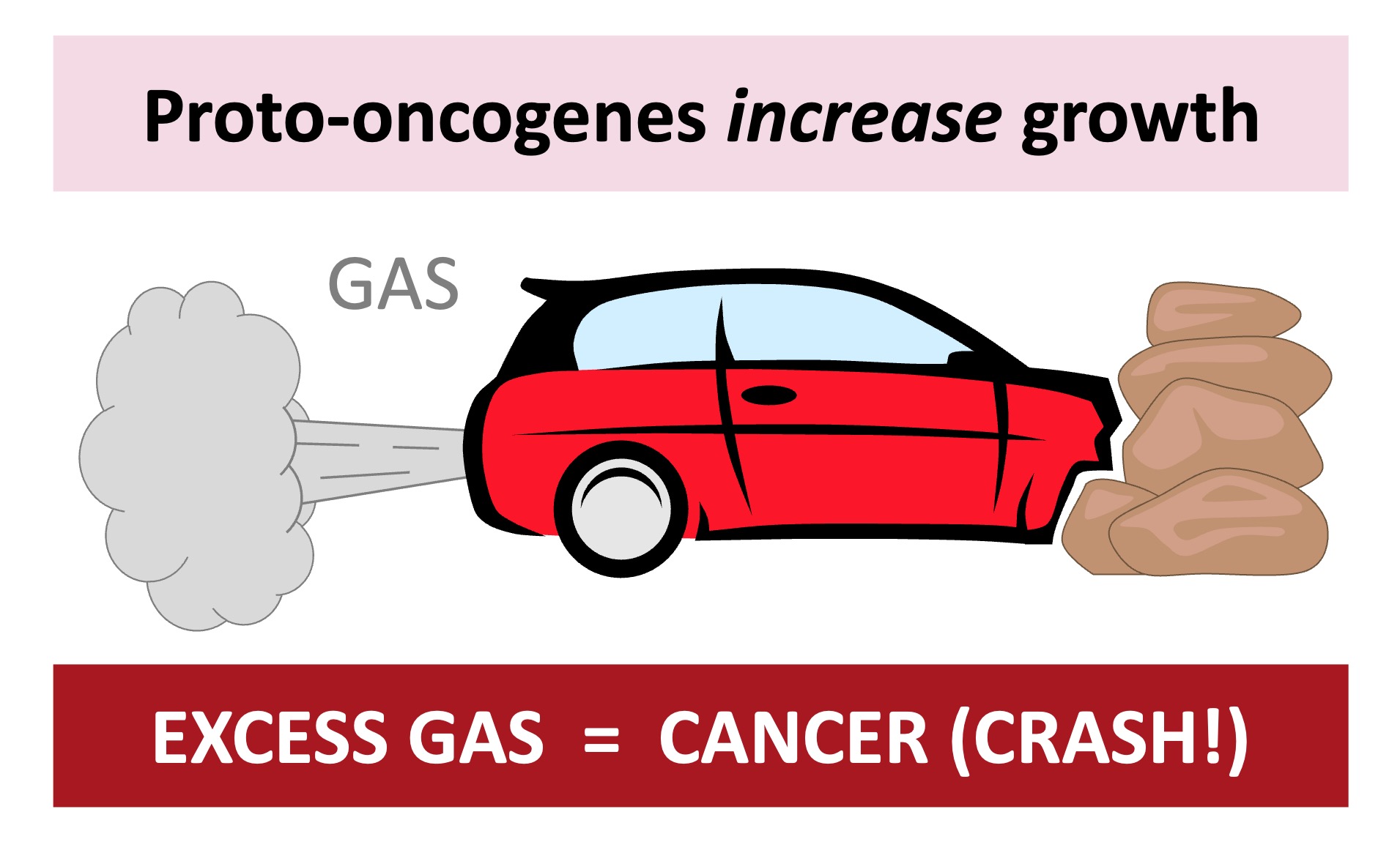
Proto-oncogenes code for proteins that stimulate the cell cycle and promote cell growth and proliferation
-
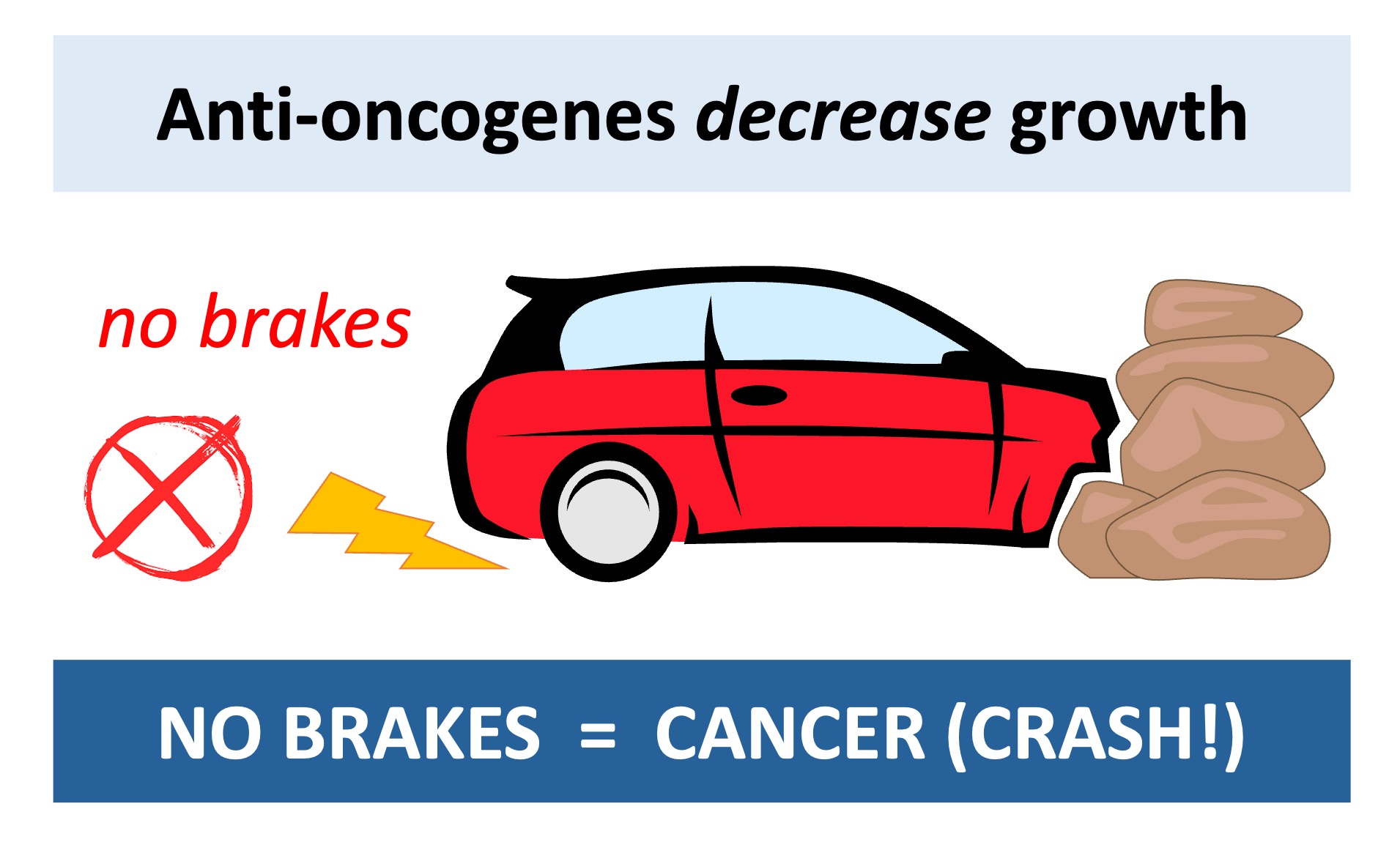
Tumour suppressor genes code for proteins that repress cell cycle progression and promote apoptosis
When a proto-oncogene is mutated or subjected to increased expression it becomes an oncogene (cancer-causing gene)
-
Tumour suppressor genes are sometimes referred to as anti-oncogenes, as their normal function prevents cancer
Cancer-Causing Mutations