Artificial Selection
Allele frequencies can be changed by artificial selection, whereby man intervenes in the breeding of species to produce desired traits in offspring
-
By breeding members of a species with a desired trait, the trait becomes more pronounced across successive generations, allowing for significant phenotypic changes in a (relatively) short period
Selective breeding of crop plants has allowed for the generation of new types of foods from the same ancestral plant source
-
The wild mustard plant (genus Brassica) has been bred to produce different foods by modifying plant sections through artificial selection
-
This has resulted in foods such as broccoli (modified flower buds), cabbage (modified leaf buds) and kale (modified leaves)
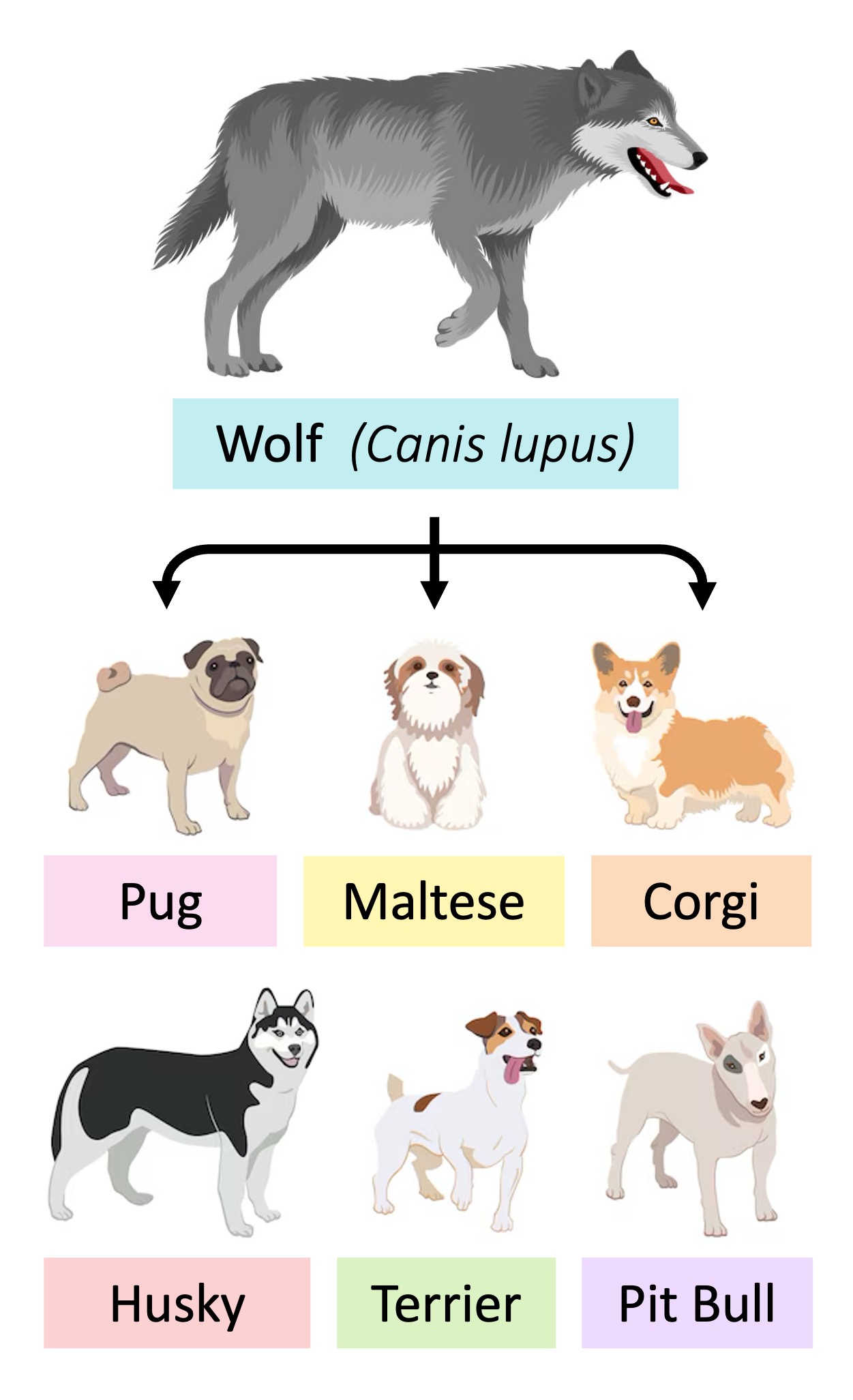
Selective breeding of domesticated animals has also resulted in the generation of diverse breeds of offspring
-
Race horses (speed) are typically leaner, taller and quicker – while draft horses (power / endurance) are sturdier and stockier
-
Dogs have been bred for a variety of purposes – including fox hunting (beagles), herding (sheep dogs), racing (greyhounds) and size (chihuahuas)
Artificial selection only occurs when humans make deliberate choices regarding the evolution of specific traits
-
Unintended consequences of human actions, such as the evolution of resistance in bacteria when an antibiotic is used, are due to natural selection
Artificial Selection

Agricultural Crops