Apical Growth
Apical growth refers to the growth that occurs at the tips of a plant’s shoots and roots and is controlled by two phytohormones
-
Auxin is responsible for cell elongation and is produced in the shoot tips of a plant
-
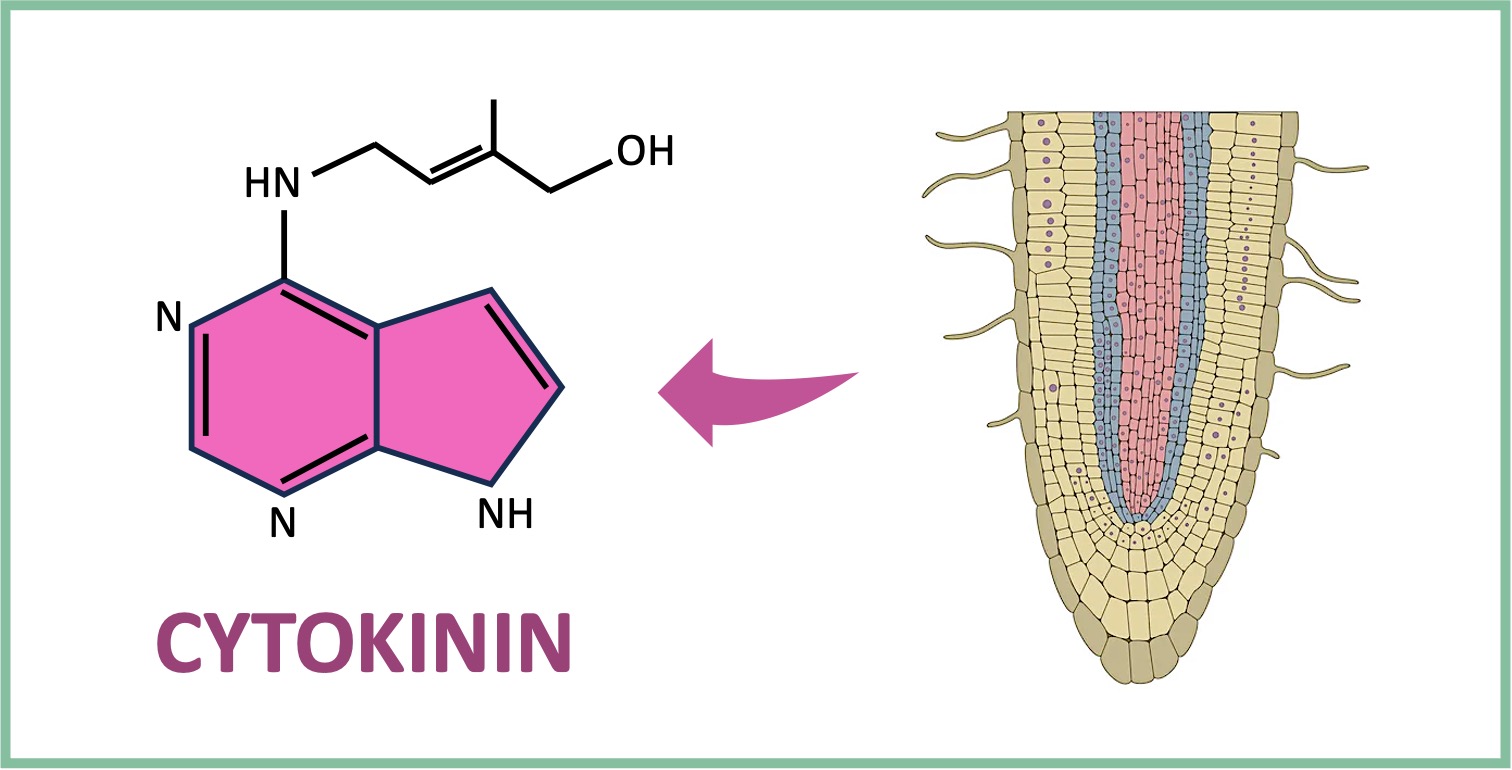
Cytokinin is responsible for cell division and is produced in the root tips of a plant
Both hormones are required for apical growth and must be transported to the region of the plant where they are not produced
-
Auxins are transported from the plant shoots towards the roots (downwards) within the sap of the phloem
-
Cytokinin is transported from the plant roots towards the shoots (upwards) within the xylem vessels
Interactions between auxin and cytokinin ensure root and shoot growth is regulated
-
Auxins promote root growth and inhibit shoot growth, while cytokinins have the reverse effect (antagonistic)
-
Differing the concentrations of the two hormones allows plants to adapt their growth to different environments and nutrient availabilities
Apical Growth Control
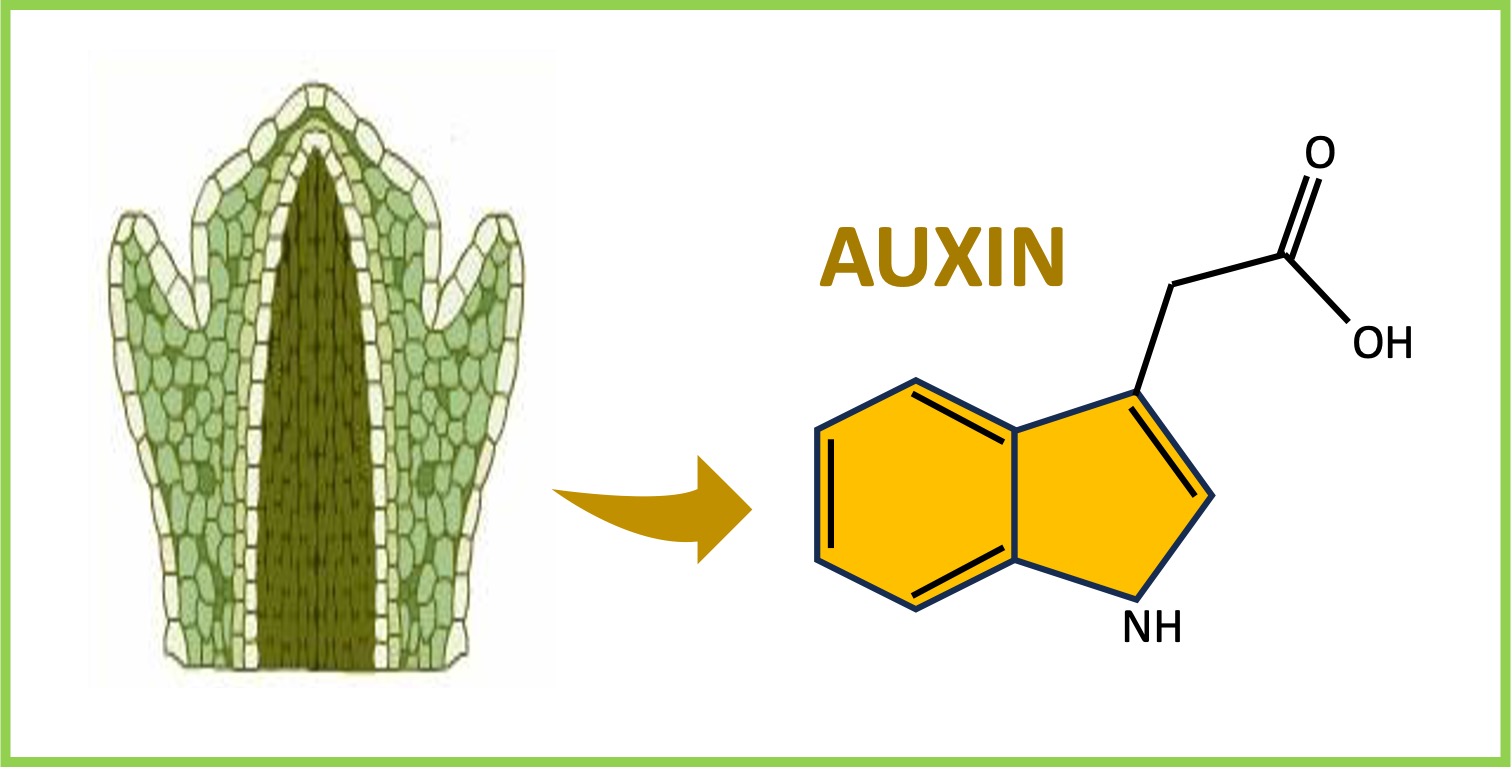
Auxin produced in shoot tip